Peptide-Alkoxyamine Drugs: An Innovative Approach to Fight Schistosomiasis: "Digging Their Graves with Their Forks"
- PMID: 38921780
- PMCID: PMC11206678
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens13060482
Peptide-Alkoxyamine Drugs: An Innovative Approach to Fight Schistosomiasis: "Digging Their Graves with Their Forks"
Erratum in
-
Correction: Embo-Ibouanga et al. Peptide-Alkoxyamine Drugs: An Innovative Approach to Fight Schistosomiasis: "Digging Their Graves with Their Forks". Pathogens 2024, 13, 482.Pathogens. 2025 Jul 8;14(7):669. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14070669. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40732767 Free PMC article.
Abstract
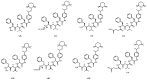
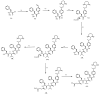
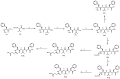
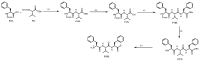
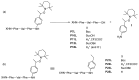
The expansion of drug resistant parasites sheds a serious concern on several neglected parasitic diseases. Our recent results on cancer led us to envision the use of peptide-alkoxyamines as a highly selective and efficient new drug against schistosome adult worms, the etiological agents of schistosomiasis. Indeed, the peptide tag of the hybrid compounds can be hydrolyzed by worm's digestive enzymes to afford a highly labile alkoxyamine which homolyzes spontaneously and instantaneously into radicals-which are then used as a drug against Schistosome adult parasites. This approach is nicely summarized as digging their graves with their forks. Several hybrid peptide-alkoxyamines were prepared and clearly showed an activity: two of the tested compounds kill 50% of the parasites in two hours at a concentration of 100 µg/mL. Importantly, the peptide and alkoxyamine fragments that are unable to generate alkyl radicals display no activity. This strong evidence validates the proposed mechanism: a specific activation of the prodrugs by the parasite proteases leading to parasite death through in situ alkyl radical generation.
Keywords: alkoxyamines; new concept; prodrug; schistosoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Jerome Boissier is the cofounder of ParaDev company that was subcontracted to carry out the antiparasitic tests on the Schistosome.
Figures
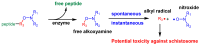


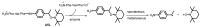
References
-
- Mouahid J., Moneé G. Schistosoma spp. In: Rose J.B., Jimeénez-Cisneros B., Robertson L., editors. Water and Sanitation for the 21st Century: Health and Microbiological Aspects of Excreta and Wastewater Management (Global Water Pathogen Project) Michigan State University; East Lansing, MI, USA: UNESCO; Paris, France: 2019. Part 3: Specific Excreted Pathogens: Environmental and Epidemiology Aspects—Section 4:, Helminths.
-
- Theétiot-Laurent S.A.-L., Boissier J., Robert A., Meunier B. A Schistosomiasis Model with Diffusion Effects. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013;52:7936–7956. - PubMed
-
- Summers S., Bhattacharyya T., Allan F., Stothard J.R., Edielu A., Webster B.L., Miles M.A., Bustinduy L.A. A review of the genetic determinants of praziquantel resistance in Schistosoma mansoni: Is praziquantel and intestinal schistosomiasis a perfect match? Front. Trop. Dis. 2022;3:933097. doi: 10.3389/fitd.2022.933097. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

