The Current State of Proteomics and Metabolomics for Inner Ear Health and Disease
- PMID: 38921823
- PMCID: PMC11207525
- DOI: 10.3390/proteomes12020017
The Current State of Proteomics and Metabolomics for Inner Ear Health and Disease
Abstract
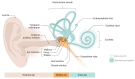
Characterising inner ear disorders represents a significant challenge due to a lack of reliable experimental procedures and identified biomarkers. It is also difficult to access the complex microenvironments of the inner ear and investigate specific pathological indicators through conventional techniques. Omics technologies have the potential to play a vital role in revolutionising the diagnosis of ear disorders by providing a comprehensive understanding of biological systems at various molecular levels. These approaches reveal valuable information about biomolecular signatures within the cochlear tissue or fluids such as the perilymphatic and endolymphatic fluid. Proteomics identifies changes in protein abundance, while metabolomics explores metabolic products and pathways, aiding the characterisation and early diagnosis of diseases. Although there are different methods for identifying and quantifying biomolecules, mass spectrometry, as part of proteomics and metabolomics analysis, could be utilised as an effective instrument for understanding different inner ear disorders. This study aims to review the literature on the application of proteomic and metabolomic approaches by specifically focusing on Meniere's disease, ototoxicity, noise-induced hearing loss, and vestibular schwannoma. Determining potential protein and metabolite biomarkers may be helpful for the diagnosis and treatment of inner ear problems.
Keywords: inner ear; mass spectrometry; meniere’s disease; metabolomics; noise-induced hearing loss; ototoxicity; proteomics; vestibular schwannoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical high-resolution imaging and grading of endolymphatic hydrops in Hydropic Ear Disease at 1.5 T using the two-slice grading for vestibular endolymphatic hydrops in less than 10 min.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 Feb;279(2):751-757. doi: 10.1007/s00405-021-06731-7. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 33687507
-
Audio-vestibular and radiological analysis in Meniere's disease.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 Nov-Dec;88 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S117-S124. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2022.08.003. Epub 2022 Oct 11. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 36257895 Free PMC article.
-
Signal Alteration of the Inner Ear on High-Resolution Three-Dimensional Constructive Interference in Steady State Sequence in Patients with Ménière's Disease and Labyrinthitis.Audiol Neurootol. 2022;27(6):449-457. doi: 10.1159/000525419. Epub 2022 Aug 29. Audiol Neurootol. 2022. PMID: 36037798 Free PMC article.
-
Brain and inner-ear fluid homeostasis, cochleovestibular-type tinnitus, and secondary endolymphatic hydrops.Int Tinnitus J. 2006;12(1):75-81. Int Tinnitus J. 2006. PMID: 17147045 Review.
-
[Menière's Disease].Laryngorhinootologie. 2015 Aug;94(8):530-54. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1555808. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Laryngorhinootologie. 2015. PMID: 26243634 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Quantitative Proteomics of Cochlear Tissues: Bilateral Comparisons in Guinea Pigs and Rats.Proteomics. 2025 Jun 23;25(13):e13977. doi: 10.1002/pmic.13977. Online ahead of print. Proteomics. 2025. PMID: 40545996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Srivastava S., Sivasankar G., Dua G. Review of research on environmental noise standards/policies/guidelines and measurement methodology in high-speed rail. Noise Vib. Worldw. 2022;53:487–497. doi: 10.1177/09574565221128067. - DOI
-
- Nakashima T., Sone M., Teranishi M., Yoshida T., Terasaki H., Kondo M., Yasuma T., Wakabayashi T., Nagatani T., Naganawa S. A perspective from magnetic resonance imaging findings of the inner ear: Relationships among cerebrospinal, ocular and inner ear fluids. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2012;39:345–355. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2011.05.005. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources