Acute and Long-Term Effects of Stretching with Whole-Body Vibration on Young's Modulus of the Soleus Muscle Measured Using Shear Wave Elastography
- PMID: 38921859
- PMCID: PMC11209423
- DOI: 10.3390/sports12060165
Acute and Long-Term Effects of Stretching with Whole-Body Vibration on Young's Modulus of the Soleus Muscle Measured Using Shear Wave Elastography
Abstract
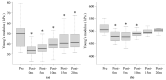
The effect of whole-body vibration (WBV) stretching on soleus (SOL) muscle stiffness remains unclear. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the acute and long-term effects of stretching with WBV on SOL muscle stiffness. This study employed a repeated-measures experimental design evaluating 20 healthy young males. SOL muscle stretching with WBV was performed for 5 min per day (1 min per set, five sets) over 4 weeks, for 4 days a week. Participants stretched the SOL muscle with ankle dorsiflexion in a loaded flexed knee position on a WBV device. Data were obtained to examine acute effects before stretching, immediately after stretching, and at 5, 10, 15, and 20 min. Moreover, data were obtained to examine the long-term effects before stretching, immediately after the completion of the 4-week stretching program, and at 2 and 4 weeks later. SOL muscle stiffness was measured using Young's modulus with shear wave elastography. The acute effect of SOL muscle stretching with WBV persisted for up to 20 min. Additionally, the long-term effect of stretching was better maintained than the acute effect, which was effective for up to 4 weeks (p < 0.001). Clinically, continuous stretching with WBV may be used to improve SOL muscle stiffness in rehabilitation programs.
Keywords: Young’s modulus; elastography; range of motion; soleus muscle; stiffness; stretching; whole-body vibration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Absolute reliability of Young's modulus of the soleus muscle and Achilles tendon measured using shear wave elastography in healthy young males.Asia Pac J Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Technol. 2024 Apr 20;37:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.asmart.2024.04.001. eCollection 2024 Jul. Asia Pac J Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Technol. 2024. PMID: 38682074 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative evaluation of the effects of several weeks of static stretching on the flexibility of the rectus femoris using shear wave elastography: a before-after study.J Ultrason. 2024 Nov 30;24(98):1-6. doi: 10.15557/jou.2024.0025. eCollection 2024 Dec. J Ultrason. 2024. PMID: 39619262 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship Between the Amount of Change in Echo Intensity and Young's Modulus of the Soleus Muscle After Ankle Fracture Surgery.Cureus. 2024 Oct 29;16(10):e72624. doi: 10.7759/cureus.72624. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39610620 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle-specific acute changes in passive stiffness of human triceps surae after stretching.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2016 May;116(5):911-8. doi: 10.1007/s00421-016-3349-3. Epub 2016 Mar 5. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26945574
-
Effects of Whole-Body Vibration on Flexibility and Stiffness: A Literature Review.Int J Exerc Sci. 2019 May 1;12(3):735-747. doi: 10.70252/TJVC4921. eCollection 2019. Int J Exerc Sci. 2019. PMID: 31156749 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Can measurement errors explain variance in the relationship between muscle- and tendon stiffness and range of motion?-a blinded reliability and objectivity study.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2025 Jun 11. doi: 10.1007/s00421-025-05814-1. Online ahead of print. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40500535
References
-
- Balius R., Alomar X., Rodas G., Miguel-Pérez M., Pedret C., Dobado M.C., Blasi J., Koulouris G. The Soleus Muscle: MRI, Anatomic and Histologic Findings in Cadavers with Clinical Correlation of Strain Injury Distribution. Skeletal Radiol. 2013;42:521–530. doi: 10.1007/s00256-012-1513-3. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

