Synthesis and Characterization of Composite WO3 Fibers/g-C3N4 Photocatalysts for the Removal of the Insecticide Clothianidin in Aquatic Media
- PMID: 38921921
- PMCID: PMC11206630
- DOI: 10.3390/nano14121045
Synthesis and Characterization of Composite WO3 Fibers/g-C3N4 Photocatalysts for the Removal of the Insecticide Clothianidin in Aquatic Media
Abstract
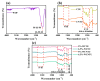
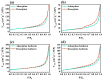
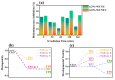
Photocatalysis is a prominent alternative wastewater treatment technique that has the potential to completely degrade pesticides as well as other persistent organic pollutants, leading to detoxification of wastewater and thus paving the way for its efficient reuse. In addition to the more conventional photocatalysts (e.g., TiO2, ZnO, etc.) that utilize only UV light for activation, the interest of the scientific community has recently focused on the development and application of visible light-activated photocatalysts like g-C3N4. However, some disadvantages of g-C3N4, such as the high recombination rate of photogenerated charges, limit its utility. In this light, the present study focuses on the synthesis of WO3 fibers/g-C3N4 Z-scheme heterojunctions to improve the efficiency of g-C3N4 towards the photocatalytic removal of the widely used insecticide clothianidin. The effect of two different g-C3N4 precursors (urea and thiourea) and of WO3 fiber content on the properties of the synthesized composite materials was also investigated. All aforementioned materials were characterized by a number of techniques (XRD, SEM-EDS, ATR-FTIR, Raman spectroscopy, DRS, etc.). According to the results, mixing 6.5% W/W WO3 fibers with either urea or thiourea derived g-C3N4 significantly increased the photocatalytic activity of the resulting composites compared to the precursor materials. In order to further elucidate the effect of the most efficient composite photocatalyst in the degradation of clothianidin, the generated transformation products were tentatively identified through UHPLC tandem high-resolution mass spectroscopy. Finally, the detoxification effect of the most efficient process was also assessed by combining the results of an in-vitro methodology and the predictions of two in-silico tools.
Keywords: AOPs; Z-scheme; graphitic carbon nitride; photocatalysis; toxicity assessment; transformation products.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
The Synthesis of h-BN-Modified Z-Scheme WO3/g-C3N4 Heterojunctions for Enhancing Visible Light Photocatalytic Degradation of Tetracycline Pollutants.ACS Omega. 2022 Feb 10;7(7):6035-6045. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c06377. eCollection 2022 Feb 22. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35224364 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication and Characterization of Highly Efficient As-Synthesized WO3/Graphitic-C3N4 Nanocomposite for Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Compounds.Materials (Basel). 2022 Mar 28;15(7):2482. doi: 10.3390/ma15072482. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35407814 Free PMC article.
-
Visible-light-induced WO3/g-C3N4 composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity.Dalton Trans. 2013 Jun 28;42(24):8606-16. doi: 10.1039/c3dt00115f. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Dalton Trans. 2013. PMID: 23629048
-
Graphitic Carbon Nitride/Zinc Oxide-Based Z-Scheme and S-Scheme Heterojunction Photocatalysts for the Photodegradation of Organic Pollutants.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 9;24(19):15021. doi: 10.3390/ijms241915021. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Graphitic Carbon Nitride (g-C3N4)-Metal Oxide-Based Nanocomposites: Potential for Photocatalysis and Sensing.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Jan 17;12(2):294. doi: 10.3390/nano12020294. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35055311 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hierarchical WS2-WO3 Nanohybrids with Flower-like p-n Heterostructures for Trimethylamine Detection.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Aug 6;14(16):1322. doi: 10.3390/nano14161322. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39195361 Free PMC article.
-
A review on WO3 photocatalysis used for wastewater treatment and pesticide degradation.Heliyon. 2024 Dec 13;11(1):e40788. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40788. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39811338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Influence Mechanism of Dissolved Organic Matter on the Photocatalytic Oxidation of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products.Molecules. 2025 May 22;30(11):2266. doi: 10.3390/molecules30112266. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40509152 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Intisar A., Ramzan A., Hafeez S., Hussain N., Irfan M., Shakeel N., Gill K.A., Iqbal A., Janczarek M., Jesionowski T. Adsorptive and Photocatalytic Degradation Potential of Porous Polymeric Materials for Removal of Pesticides, Pharmaceuticals, and Dyes-Based Emerging Contaminants from Water. Chemosphere. 2023;336:139203. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.139203. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Luo Y., Guo W., Ngo H.H., Nghiem L.D., Hai F.I., Zhang J., Liang S., Wang X.C. A Review on the Occurrence of Micropollutants in the Aquatic Environment and Their Fate and Removal during Wastewater Treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014;473–474:619–641. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.12.065. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

