Advanced Photocatalytic Degradation of Cytarabine from Pharmaceutical Wastewaters
- PMID: 38922085
- PMCID: PMC11209206
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics12060405
Advanced Photocatalytic Degradation of Cytarabine from Pharmaceutical Wastewaters
Abstract
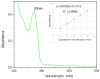
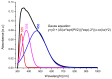
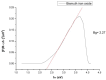
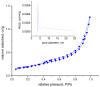
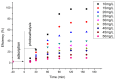
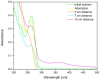
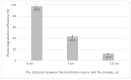
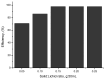
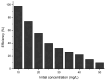
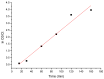
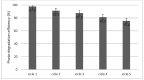
The need to develop advanced wastewater treatment techniques and their use has become a priority, the main goal being the efficient removal of pollutants, especially those of organic origin. This study presents the photo-degradation of a pharmaceutical wastewater containing Kabi cytarabine, using ultraviolet (UV) radiation, and a synthesized catalyst, a composite based on bismuth and iron oxides (BFO). The size of the bandgap was determined by UV spectroscopy, having a value of 2.27 eV. The specific surface was determined using the BET method, having a value of 0.7 m2 g-1. The material studied for the photo-degradation of cytarabine presents a remarkable photo-degradation efficiency of 97.9% for an initial concentration 0f 10 mg/L cytarabine Kabi when 0.15 g of material was used, during 120 min of interaction with UV radiation at 3 cm from the irradiation source. The material withstands five photo-degradation cycles with good results. At the same time, through this study, it was possible to establish that pyrimidine derivatives could be able to combat infections caused by Escherichia coli and Candida parapsilosis.
Keywords: UV radiation; cytarabine Kabi; degradation; kinetic process.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synthesis of new hybrid composite based on TiO2 for photo-catalytic degradation of sulfamethoxazole and pharmaceutical wastewater, optimization, performance, and reaction mechanism studies.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Aug;29(37):56403-56418. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-19375-9. Epub 2022 Mar 25. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35334054
-
Photochemical degradation and mineralization of 4-chlorophenol.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2003;10(2):113-20. doi: 10.1065/espr2002.10.135. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2003. PMID: 12729044
-
Removal of β-lactam antibiotics from pharmaceutical wastewaters using photo-Fenton process at near-neutral pH.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Jul;25(21):20293-20303. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-8420-z. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 28160176
-
A review on the photoelectro-Fenton process as efficient electrochemical advanced oxidation for wastewater remediation. Treatment with UV light, sunlight, and coupling with conventional and other photo-assisted advanced technologies.Chemosphere. 2020 Jul;250:126198. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126198. Epub 2020 Feb 17. Chemosphere. 2020. PMID: 32105855 Review.
-
Advanced oxidation process for the treatment of industrial wastewater: A review on strategies, mechanisms, bottlenecks and prospects.Chemosphere. 2023 Dec;345:140473. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.140473. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Chemosphere. 2023. PMID: 37866496 Review.
References
-
- Xie H. Occurrence, Ecotoxicology, and Treatment of Anticancer Agents as Water Contaminants. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2012;2:1–11. doi: 10.4172/2161-0525.S2-002. - DOI
-
- Ocampo-Pérez R., Sánchez-Polo M., Rivera-Utrilla J., Leyva-Ramos R. Degradation of antineoplastic cytarabine in aqueous phase by advanced oxidation processes based on ultraviolet radiation. Chem. Eng. J. 2010;165:581–588. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2010.09.076. - DOI
-
- Koltsakidou A., Antonopoulou M., Evgenidou E., Konstantinou I., Lambropoulou D.A. Cytarabine degradation by simulated solar assisted photocatalysis using TiO2. Chem. Eng. J. 2017;316:823–831. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.01.132. - DOI
-
- Faruqi A., Tadi P. Cytarabine. StatPearls Publishing LLC.; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2023. [(accessed on 15 January 2024)]. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557680/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

