Cited2 is a key regulator of placental development and plasticity
- PMID: 38922923
- PMCID: PMC11331489
- DOI: 10.1002/bies.202300118
Cited2 is a key regulator of placental development and plasticity
Abstract
The biology of trophoblast cell lineage development and placentation is characterized by the involvement of several known transcription factors. Central to the action of a subset of these transcriptional regulators is CBP-p300 interacting transactivator with Glu/Asp-rich carboxy-terminal domain 2 (CITED2). CITED2 acts as a coregulator modulating transcription factor activities and affecting placental development and adaptations to physiological stressors. These actions of CITED2 on the trophoblast cell lineage and placentation are conserved across the mouse, rat, and human. Thus, aspects of CITED2 biology in hemochorial placentation can be effectively modeled in the mouse and rat. In this review, we present information on the conserved role of CITED2 in the biology of placentation and discuss the use of CITED2 as a tool to discover new insights into regulatory mechanisms controlling placental development.
Keywords: CITED2; HIF1; TFAP2C; modulator; placentation; trophoblast.
© 2024 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures

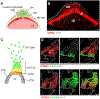
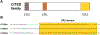

References
-
- Sun HB, Zhu YX, Yin T, Sledge G, & Yang YC (1998). MRG1, the product of a melanocyte-specific gene related gene, is a cytokine-inducible transcription factor with transformation activity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 95(23), 13555–13560. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bamforth SD, Bragança J, Eloranta JJ, Murdoch JN, Marques FI, Kranc KR, Farza H, Henderson DJ, Hurst HC, & Bhattacharya S (2001). Cardiac malformations, adrenal agenesis, neural crest defects and exencephaly in mice lacking Cited2, a new Tfap2 co-activator. Nature Genetics, 29(4), 469–474. 10.1038/ng768 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

