Implementation of First-Trimester Screening and Prevention of Preeclampsia: A Stepped Wedge Cluster-Randomized Trial in Asia
- PMID: 38923439
- PMCID: PMC11472904
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.124.069907
Implementation of First-Trimester Screening and Prevention of Preeclampsia: A Stepped Wedge Cluster-Randomized Trial in Asia
Abstract
Background: This trial aimed to assess the efficacy, acceptability, and safety of a first-trimester screen-and-prevent strategy for preterm preeclampsia in Asia.
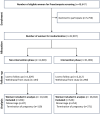
Methods: Between August 1, 2019, and February 28, 2022, this multicenter stepped wedge cluster randomized trial included maternity/diagnostic units from 10 regions in Asia. The trial started with a period where all recruiting centers provided routine antenatal care without study-related intervention. At regular 6-week intervals, one cluster was randomized to transit from nonintervention phase to intervention phase. In the intervention phase, women underwent first-trimester screening for preterm preeclampsia using a Bayes theorem-based triple-test. High-risk women, with adjusted risk for preterm preeclampsia ≥1 in 100, received low-dose aspirin from <16 weeks until 36 weeks.
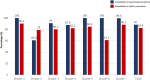
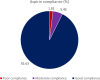
Results: Overall, 88.04% (42 897 of 48 725) of women agreed to undergo first-trimester screening for preterm preeclampsia. Among those identified as high-risk in the intervention phase, 82.39% (2919 of 3543) received aspirin prophylaxis. There was no significant difference in the incidence of preterm preeclampsia between the intervention and non-intervention phases (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.59 [95% CI, 0.91-2.77]). However, among high-risk women in the intervention phase, aspirin prophylaxis was significantly associated with a 41% reduction in the incidence of preterm preeclampsia (aOR, 0.59 [95% CI, 0.37-0.92]). In addition, it correlated with 54%, 55%, and 64% reduction in the incidence of preeclampsia with delivery at <34 weeks (aOR, 0.46 [95% CI, 0.23-0.93]), spontaneous preterm birth <34 weeks (aOR, 0.45 [95% CI, 0.22-0.92]), and perinatal death (aOR, 0.34 [95% CI, 0.12-0.91]), respectively. There was no significant between-group difference in the incidence of aspirin-related severe adverse events.
Conclusions: The implementation of the screen-and-prevent strategy for preterm preeclampsia is not associated with a significant reduction in the incidence of preterm preeclampsia. However, low-dose aspirin effectively reduces the incidence of preterm preeclampsia by 41% among high-risk women. The screen-and-prevent strategy for preterm preeclampsia is highly accepted by a diverse group of women from various ethnic backgrounds beyond the original population where the strategy was developed. These findings underpin the importance of the widespread implementation of the screen-and-prevent strategy for preterm preeclampsia on a global scale.
Registration: URL: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov; Unique identifier: NCT03941886.
Keywords: Asia; Fetal Medicine Foundation; aspirin; first-trimester; preeclampsia; screen-and-prevent; screening; stepped wedge cluster randomized trial.
Conflict of interest statement
L.C.P. has received speaker fees and consultancy payments from Roche Diagnostics and Ferring Pharmaceuticals. In addition, she has received in-kind contributions from Roche Diagnostics, Revvity Inc (formerly PerkinElmer Life and Analytical Sciences), Thermo Fisher Scientific, Ningbo Aucheer Biological Technology Co, Ltd, and GE HealthCare. D.S.S. has received in-kind contributions from Revvity Inc, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Roche Diagnostics, Diabetomics, and Ningbo Aucheer Biological Technology Co, Ltd. R.K.P. is chief executive officer of Ritz Medical Co Ltd, a genetic testing company, and holds shares in and receives executive compensation from it. The other authors report no conflicts.
Figures
References
-
- Steegers EA, von Dadelszen P, Duvekot JJ, Pijnenborg R. Pre-eclampsia. Lancet. 2010;376:631–644. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60279-6 - PubMed
-
- Mol BWJ, Roberts CT, Thangaratinam S, Magee LA, de Groot CJM, Hofmeyr GJ. Pre-eclampsia. Lancet. 2016;387:999–1011. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00070-7 - PubMed
-
- Chaemsaithong P, Pooh RK, Zheng M, Ma R, Chaiyasit N, Tokunaka M, Shaw SW, Seshadri S, Choolani M, Wataganara T, et al. . Prospective evaluation of screening performance of first-trimester prediction models for preterm preeclampsia in an Asian population. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;221:650.e1–650.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2019.09.041 - PubMed
-
- Say L, Chou D, Gemmill A, Tunçalp O, Moller A-B, Daniels J, Gülmezoglu AM, Temmerman M, Alkema L. Global causes of maternal death: a WHO systematic analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2014;2:e323–e333. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(14)70227-X - PubMed
-
- Poon LC, Shennan A, Hyett JA, Kapur A, Hadar E, Divakar H, McAuliffe F, da Silva Costa F, von Dadelszen P, McIntyre HD, et al. . The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) initiative on pre-eclampsia: a pragmatic guide for first-trimester screening and prevention. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2019;145:1–33. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.12802 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical