Electroacupuncture Promotes Liver Regeneration by Activating DMV Acetylcholinergic Neurons-Vagus-Macrophage Axis in 70% Partial Hepatectomy of Mice
- PMID: 38923873
- PMCID: PMC11348175
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202402856
Electroacupuncture Promotes Liver Regeneration by Activating DMV Acetylcholinergic Neurons-Vagus-Macrophage Axis in 70% Partial Hepatectomy of Mice
Abstract
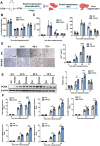
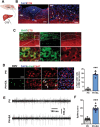
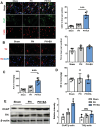
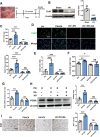
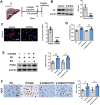
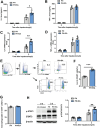
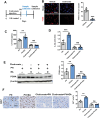
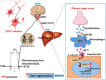
Lack of liver regenerative capacity is the primary cause of hepatic failure and even mortality in patients undergoing hepatectomy, with no effective intervention strategies currently available. Therefore, identifying efficacious interventions to enhance liver regeneration is pivotal for optimizing clinical outcomes. Recent studies have demonstrated that vagotomy exerts an inhibitory effect on liver regeneration following partial hepatectomy, thereby substantiating the pivotal role played by the vagus nerve in the process of liver regeneration. In recent years, electroacupuncture (EA) has emerged as a non-invasive technique for stimulating the vagus nerve. However, EA on hepatic regeneration remains uncertain. In this study, a 70% partial hepatectomy (PH) mouse model is utilized to investigate the effects of EA on acute liver regeneration and elucidate its underlying molecular mechanisms. It is observed that EA at ST36 acutely activated cholinergic neurons in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve (DMV), resulting in increased release of acetylcholine from hepatic vagal nerve endings and subsequent activation of IL-6 signaling in liver macrophages. Ultimately, these events promoted hepatocyte proliferation and facilitated liver regeneration. These findings provide insights into the fundamental brain-liver axis mechanism through which EA promotes liver regeneration, offering a novel therapeutic approach for post-hepatectomy liver regeneration disorders.
Keywords: acetylcholinergic neurons; dorsal motor nucleus of vagus; electroacupuncture; liver regeneration; vagus nerve.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Comment in
-
Electroacupuncture in liver regeneration: a Chinese traditional medicine approach to enhancing liver regeneration.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2024 Oct 1;13(5):891-893. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-24-516. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39507731 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Michalopoulos G. K., Bhushan B., Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 40. - PubMed
-
- Huang R., Zhang X., Gracia‐Sancho J., Xie W. F., Liver Int. 2022, 42, 1486. - PubMed
-
- Ozaki M., Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 100, 62. - PubMed
-
- Forbes S. J., Newsome P. N., Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 473. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 82370582/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 201940352/Scientific Program of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission
- 22ZR1428100/Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality
- 22YF1449600/Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality
- 22ZR1462300/Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Commission
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
