Gene-environment interactions within a precision environmental health framework
- PMID: 38925123
- PMCID: PMC11293590
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xgen.2024.100591
Gene-environment interactions within a precision environmental health framework
Abstract
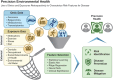
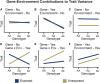
Understanding the complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors in disease etiology and the role of gene-environment interactions (GEIs) across human development stages is important. We review the state of GEI research, including challenges in measuring environmental factors and advantages of GEI analysis in understanding disease mechanisms. We discuss the evolution of GEI studies from candidate gene-environment studies to genome-wide interaction studies (GWISs) and the role of multi-omics in mediating GEI effects. We review advancements in GEI analysis methods and the importance of large-scale datasets. We also address the translation of GEI findings into precision environmental health (PEH), showcasing real-world applications in healthcare and disease prevention. Additionally, we highlight societal considerations in GEI research, including environmental justice, the return of results to participants, and data privacy. Overall, we underscore the significance of GEI for disease prediction and prevention and advocate for integrating the exposome into PEH omics studies.
Keywords: environmental exposures; environmental justice; epidemiology; epigenetics; gene-environment interactions; genetics; precision environmental health.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bononi A., Goto K., Ak G., Yoshikawa Y., Emi M., Pastorino S., Carparelli L., Ferro A., Nasu M., Kim J.H., et al. Heterozygous germline BLM mutations increase susceptibility to asbestos and mesothelioma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2020;117:33466–33473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2019652117. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Modafferi S., Zhong X., Kleensang A., Murata Y., Fagiani F., Pamies D., Hogberg H.T., Calabrese V., Lachman H., Hartung T., Smirnova L. Gene-environment interactions in developmental neurotoxicity: a case study of synergy between chlorpyrifos and CHD8 knockout in human brainspheres. Environ. Health Perspect. 2021;129:77001. doi: 10.1289/ehp8580. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rampersaud E., Mitchell B.D., Pollin T.I., Fu M., Shen H., O'Connell J.R., Ducharme J.L., Hines S., Sack P., Naglieri R., et al. Physical activity and the association of common FTO gene variants with body mass index and obesity. Arch. Intern. Med. 2008;168:1791–1797. doi: 10.1001/archinte.168.16.1791. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

