ephrin-B2 promotes nociceptive plasticity and hyperalgesic priming through EphB2-MNK-eIF4E signaling in both mice and humans
- PMID: 38925462
- PMCID: PMC12230984
- DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107284
ephrin-B2 promotes nociceptive plasticity and hyperalgesic priming through EphB2-MNK-eIF4E signaling in both mice and humans
Abstract
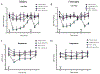
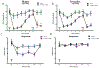
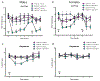
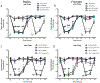
Ephrin-B-EphB signaling can promote pain through ligand-receptor interactions between peripheral cells, like immune cells expressing ephrin-Bs, and EphB receptors expressed by DRG neurons. Previous studies have shown increased ephrin-B2 expression in peripheral tissues like synovium of rheumatoid and osteoarthritis patients, indicating the clinical significance of this signaling. The primary goal of this study was to understand how ephrin-B2 acts on mouse and human DRG neurons, which express EphB receptors, to promote pain and nociceptor plasticity. We hypothesized that ephrin-B2 would promote nociceptor plasticity and hyperalgesic priming through MNK-eIF4E signaling, a critical mechanism for nociceptive plasticity induced by growth factors, cytokines and nerve injury. Both male and female mice developed dose-dependent mechanical hypersensitivity in response to ephrin-B2, and both sexes showed hyperalgesic priming when challenged with PGE2 injection either to the paw or the cranial dura. Acute nociceptive behaviors and hyperalgesic priming were blocked in mice lacking MNK1 (Mknk1 knockout mice) and by eFT508, a specific MNK inhibitor. Sensory neuron-specific knockout of EphB2 using Pirt-Cre demonstrated that ephrin-B2 actions require this receptor. In Ca2+-imaging experiments on cultured DRG neurons, ephrin-B2 treatment enhanced Ca2+ transients in response to PGE2 and these effects were absent in DRG neurons from MNK1-/- and EphB2-PirtCre mice. In experiments on human DRG neurons, ephrin-B2 increased eIF4E phosphorylation and enhanced Ca2+ responses to PGE2 treatment, both blocked by eFT508. We conclude that ephrin-B2 acts directly on mouse and human sensory neurons to induce nociceptor plasticity via MNK-eIF4E signaling, offering new insight into how ephrin-B signaling promotes pain.
Keywords: EphB; Ephrin; MNK1; MNK2; acute to chronic pain; hyperalgesic priming; nociceptor.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest TJP is a founder of 4E Therapeutics, a company developing MNK inhibitors for the treatment of pain. The authors declare no other conflicts of interest.
Figures
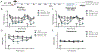

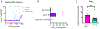
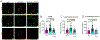
References
-
- Antonova M, Wienecke T, Olesen J, Ashina M. Prostaglandin E2 induces immediate migraine-like attack in migraine patients without aura. The Journal of Headache and Pain 2013;14(1):P113. - PubMed
-
- Ashina M, Katsarava Z, Do TP, Buse DC, Pozo-Rosich P, Ozge A, Krymchantowski AV, Lebedeva ER, Ravishankar K, Yu S, Sacco S, Ashina S, Younis S, Steiner TJ, Lipton RB. Migraine: epidemiology and systems of care. Lancet 2021;397(10283):1485–1495. - PubMed
-
- Asiedu MN, Tillu DV, Melemedjian OK, Shy A, Sanoja R, Bodell B, Ghosh S, Porreca F, Price TJ. Spinal protein kinase M zeta underlies the maintenance mechanism of persistent nociceptive sensitization. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 2011;31(18):6646–6653. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

