The role of hsa-miR-193a-5p as an important factor for control of inositol in alopecia areata
- PMID: 38925555
- PMCID: PMC11197030
- DOI: 10.1111/srt.13800
The role of hsa-miR-193a-5p as an important factor for control of inositol in alopecia areata
Erratum in
-
Correction to "the Role of Hsa-miR-193a-5p as an Important Factor for Control of Inositol in Alopecia Areata".Skin Res Technol. 2025 Aug;31(8):e70212. doi: 10.1111/srt.70212. Skin Res Technol. 2025. PMID: 40745518 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small RNA molecules that play a regulatory role in various biological processes by acting as intracellular mediators. They hold great potential as therapeutic agents for targeting human disease pathways; however, there is still much to be uncovered about their mechanism of gene regulation. Alopecia areata (AA) is a commonly occurring inflammatory condition characterized by the infiltration of T cells that specifically target the anagen-stage hair follicle. The limited understanding of its precise cellular mechanism may be the reason behind the scarcity of effective treatments for AA.
Aim: The significance and function of hsa-miR-193a-5p as a genetic marker for AA and its potential influence on the advancement of the disease.
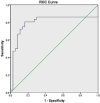
Subjects and methods: A case-control study comprised 77 individuals diagnosed with AA who were matched with 75 healthy controls. In order to measure the expression of miR-200c-3p in both groups, the real-time PCR technique was utilized. The prediction of suitable genes for hsa-miR-193a-5p, as well as the identification of pathways and gene-gene interactions, were carried out using bioinformatic tools.
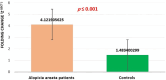
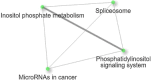
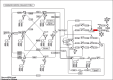
Results: The levels of hsa-miR-193a-5p expression were notably elevated in AA patients in comparison to healthy controls. Our prediction suggests that the involvement of hsa-miR-193a-5p in the development of AA is significant due to its influence on the inositol phosphorylation pathway and the Phosphatidylinositol signaling system, achieved through its direct impact on the IPPK gene.
Conclusion: For the first time, our study demonstrates the significant over-expression of a new miRNA, hsa-miR-193a-5p, in the blood of AA patients compared to controls, and highlights its impact on the IPPK gene and the inositol phosphorylation and Phosphatidylinositol signaling pathways, suggesting a potential therapeutic role for hsa-miR-193a-5p in AA.
Keywords: IPPK; alopecia areata; hsa‐miR‐193a‐5p; inositol.
© 2024 The Author(s). Skin Research and Technology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Sundberg JP, Silva KA, Li R, Cox GA, King LE. Adult‐onset Alopecia areata is a complex polygenic trait in the C3H/HeJ mouse model. J Invest Dermatol. 2004;123:294–297. - PubMed
-
- Alessandrini A, Bruni F, Piraccini BM, Starace M. Common causes of hair loss—clinical manifestations, trichoscopy and therapy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:629–640. - PubMed
-
- Rossi A, Fortuna MC, Pranteda G, et al. Clinical, histological and trichoscopic correlations in scalp disorders. Dermatology. 2015;231:201–208. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

