Detecting the FLJ22447 lncRNA in Ovarian Cancer with Cyclopentane-Modified FIT-PNAs (cpFIT-PNAs)
- PMID: 38927013
- PMCID: PMC11202290
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14060609
Detecting the FLJ22447 lncRNA in Ovarian Cancer with Cyclopentane-Modified FIT-PNAs (cpFIT-PNAs)
Abstract
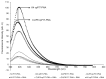
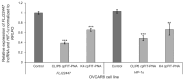
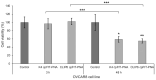
Ovarian cancer (OC) is one of the most lethal gynecologic cancers that is typically diagnosed at the very late stage of disease progression. Thus, there is an unmet need to develop diagnostic probes for early detection of OC. One approach may rely on RNA as a molecular biomarker. In this regard, FLJ22447 lncRNA is an RNA biomarker that is over-expressed in ovarian cancer (OC) and in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs). CAFs appear early on in OC as they provide a metastatic niche for OC progression. FIT-PNAs (forced intercalation-peptide nucleic acids) are DNA analogs that are designed to fluoresce upon hybridization to their complementary RNA target sequence. In recent studies, we have shown that the introduction of cyclopentane PNAs into FIT-PNAs (cpFIT-PNA) results in superior RNA sensors. Herein, we report the design and synthesis of cpFIT-PNAs for the detection of this RNA biomarker in living OC cells (OVCAR8) and in CAFs. cpFIT-PNA was compared to FIT-PNA and the cell-penetrating peptide (CPP) of choice was either a simple one (four L-lysines) or a CPP with enhanced cellular uptake (CLIP6). The combination of CLIP6 with cpFIT-PNA resulted in a superior sensing of FLJ22447 lncRNA in OVCAR8 cells as well as in CAFs. Moreover, incubation of CLIP6-cpFIT-PNA in OVCAR8 cells leads to a significant decrease (ca. 60%) in FLJ22447 lncRNA levels and in cell viability, highlighting the potential theranostic use of such molecules.
Keywords: FLJ22447 lncRNA; RNA biomarker; cancer-associated fibroblasts; cell-penetrating peptide; cyclopentane modified FIT-PNA; ovarian cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Cyclopentane FIT-PNAs: bright RNA sensors.Chem Commun (Camb). 2021 Jan 14;57(4):540-543. doi: 10.1039/d0cc07400d. Epub 2020 Dec 18. Chem Commun (Camb). 2021. PMID: 33336664
-
A Biotinylated cpFIT-PNA Platform for the Facile Detection of Drug Resistance to Artemisinin in Plasmodium falciparum.ACS Sens. 2024 Mar 22;9(3):1458-1464. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.3c02553. Epub 2024 Mar 6. ACS Sens. 2024. PMID: 38446423 Free PMC article.
-
FIT-PNAs as RNA-Sensing Probes for Drug-Resistant Plasmodium falciparum.ACS Sens. 2022 Jan 28;7(1):50-59. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.1c01481. Epub 2022 Jan 5. ACS Sens. 2022. PMID: 34985283
-
Peptide-nucleic acids (PNAs): a tool for the development of gene expression modifiers.Curr Pharm Des. 2001 Nov;7(17):1839-62. doi: 10.2174/1381612013397087. Curr Pharm Des. 2001. PMID: 11562312 Review.
-
Peptide nucleic acids: Advanced tools for biomedical applications.J Biotechnol. 2017 Oct 10;259:148-159. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.07.026. Epub 2017 Jul 29. J Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28764969 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bahramian S., Sahebi R., Roohinejad Z., Delshad E., Javid N., Amini A., Razavi A.E., Shafiee M., Shamsabadi F.T. Low expression of lncRNA-CAF attributed to the high expression of HIF1A in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and gastric cancer patients. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022;49:895–905. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06882-0. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

