When Chromatin Decondensation Affects Nuclear γH2AX Foci Pattern and Kinetics and Biases the Assessment of DNA Double-Strand Breaks by Immunofluorescence
- PMID: 38927105
- PMCID: PMC11201768
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14060703
When Chromatin Decondensation Affects Nuclear γH2AX Foci Pattern and Kinetics and Biases the Assessment of DNA Double-Strand Breaks by Immunofluorescence
Abstract
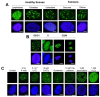
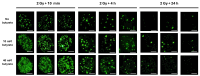
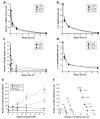
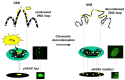
Immunofluorescence with antibodies against phosphorylated forms of H2AX (γH2AX) is revolutionizing our understanding of repair and signaling of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). Unfortunately, the pattern of γH2AX foci depends upon a number of parameters (nature of stress, number of foci, radiation dose, repair time, cell cycle phase, gene mutations, etc…) whose one of the common points is chromatin condensation/decondensation. Here, we endeavored to demonstrate how chromatin conformation affects γH2AX foci pattern and influences immunofluorescence signal. DSBs induced in non-transformed human fibroblasts were analyzed by γH2AX immunofluorescence with sodium butyrate treatment of chromatin applied after the irradiation that decondenses chromatin but does not induce DNA breaks. Our data showed that the pattern of γH2AX foci may drastically change with the experimental protocols in terms of size and brightness. Notably, some γH2AX minifoci resulting from the dispersion of the main signal due to chromatin decondensation may bias the quantification of the number of DSBs. We proposed a model called "Christmas light models" to tentatively explain this diversity of γH2AX foci pattern that may also be considered for any DNA damage marker that relocalizes as nuclear foci.
Keywords: ATM; DNA double-strand breaks; chromatin condensation; immunofluorescence; sodium butyrate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A minority of foci or pan-nuclear apoptotic staining of gammaH2AX in the S phase after UV damage contain DNA double-strand breaks.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Apr 13;107(15):6870-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1002175107. Epub 2010 Mar 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20351298 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of elimination of phosphorylated histone H2AX from chromatin after repair of DNA double-strand breaks.Mutat Res. 2010 Mar 1;685(1-2):54-60. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2009.08.001. Epub 2009 Aug 12. Mutat Res. 2010. PMID: 19682466 Review.
-
Evaluation of the spatial distribution of gammaH2AX following ionizing radiation.J Vis Exp. 2010 Aug 7;(42):2203. doi: 10.3791/2203. J Vis Exp. 2010. PMID: 20736911 Free PMC article.
-
MeCP2 deficiency leads to the γH2AX nano foci expansion after ionizing radiation.DNA Repair (Amst). 2025 Jan;145:103790. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2024.103790. Epub 2024 Nov 23. DNA Repair (Amst). 2025. PMID: 39647429
-
Does gammaH2AX foci formation depend on the presence of DNA double strand breaks?Cancer Lett. 2005 Nov 18;229(2):171-9. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2005.07.016. Epub 2005 Aug 29. Cancer Lett. 2005. PMID: 16129552 Review.
Cited by
-
Skin Fibroblasts from Individuals Self-Diagnosed as Electrosensitive Reveal Two Distinct Subsets with Delayed Nucleoshuttling of the ATM Protein in Common.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 16;26(10):4792. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104792. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abend M., Badie C., Quintens R., Kriehuber R., Manning G., Macaeva E., Njima M., Oskamp D., Strunz S., Moertl S., et al. Examining Radiation-Induced In Vivo and In Vitro Gene Expression Changes of the Peripheral Blood in Different Laboratories for Biodosimetry Purposes: First RENEB Gene Expression Study. Radiat. Res. 2016;185:109–123. doi: 10.1667/RR14221.1. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

