Ovarian Stem Cells for Women's Infertility: State of the Art
- PMID: 38927346
- PMCID: PMC11200641
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12061139
Ovarian Stem Cells for Women's Infertility: State of the Art
Abstract
Today, women's infertility is considered a social disease in females, occurring not only as an effect of POF (premature ovarian failure) but also as CTRI (cancer treatment-related infertility) in oncologic patients. Several procedures for FP (fertility preservation) are currently adopted to prevent this condition, mostly based on utilization of retrieved eggs from the patients with subsequent IVF (in vitro fertilization) or cryopreservation. However, great interest has recently been devoted to OSCs (ovarian stem cells), whose isolation from female ovaries, followed by their in vitro culture, led to their maturation to OLCs (oocyte-like cells), namely, neo-oocytes comparable to viable eggs suitable for IVF. Translation of these data to FP clinical application creates new hope in the treatment of infertility. Thus, in line with the significant progress in using stem cells in the regenerative medicine field, neo-oogenesis via OSCs, which is currently unapplicable in fertility preservation procedures, will provide novel possibilities for young and adult females in motherhood programs in the future.
Keywords: cancer treatment-related infertility (CTRI); infertility; oocyte-like cells (OLCs); ovarian stem cells (OSCs); premature ovarian failure (POF); stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Authors Krzysztof Grettka, Katarzyna Idzik, Katarzyna Lewandowska, Ksena Świętek, Simone Palini, Franco Silvestris were employed by the company Fertilita sp. z o.o., Ruda Śląska, Poland; Globiana sp. z o.o., Katowice, Poland. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The Fertilita sp. z o.o. and Globiana sp. z o.o. had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

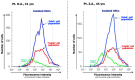
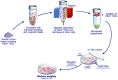

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

