Effects of Environmental Hypoxia on Serum Hematological and Biochemical Parameters, Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (hif) Gene Expression and HIF Pathway in Hybrid Sturgeon (Acipenser schrenckii ♂ × Acipenser baerii ♀)
- PMID: 38927679
- PMCID: PMC11203381
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15060743
Effects of Environmental Hypoxia on Serum Hematological and Biochemical Parameters, Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (hif) Gene Expression and HIF Pathway in Hybrid Sturgeon (Acipenser schrenckii ♂ × Acipenser baerii ♀)
Abstract
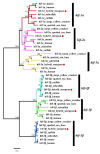
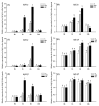
Hypoxia is a globally pressing environmental problem in aquatic ecosystems. In the present study, a comprehensive analysis was performed to evaluate the effects of hypoxia on physiological responses (hematology, cortisol, biochemistry, hif gene expression and the HIF pathway) of hybrid sturgeons (Acipenser schrenckii ♂ × Acipenser baerii ♀). A total of 180 hybrid sturgeon adults were exposed to dissolved oxygen (DO) levels of 7.00 ± 0.2 mg/L (control, N), 3.5 ± 0.2 mg/L (moderate hypoxia, MH) or 1.00 ± 0.1 mg/L (severe hypoxia, SH) and were sampled at 1 h, 6 h and 24 h after hypoxia. The results showed that the red blood cell (RBC) counts and the hemoglobin (HGB) concentration were significantly increased 6 h and 24 h after hypoxia in the SH group. The serum cortisol concentrations gradually increased with the decrease in the DO levels. Moreover, several serum biochemical parameters (AST, AKP, HBDB, LDH, GLU, TP and T-Bil) were significantly altered at 24 h in the SH group. The HIFs are transcription activators that function as master regulators in hypoxia. In this study, a complete set of six hif genes were identified and characterized in hybrid sturgeon for the first time. After hypoxia, five out of six sturgeon hif genes were significantly differentially expressed in gills, especially hif-1α and hif-3α, with more than 20-fold changes, suggesting their important roles in adaptation to hypoxia in hybrid sturgeon. A meta-analysis indicated that the HIF pathway, a major pathway for adaptation to hypoxic environments, was activated in the liver of the hybrid sturgeon 24 h after the hypoxia challenge. Our study demonstrated that hypoxia, particularly severe hypoxia (1.00 ± 0.1 mg/L), could cause considerable stress for the hybrid sturgeon. These results shed light on their adaptive mechanisms and potential biomarkers for hypoxia tolerance, aiding in aquaculture and conservation efforts.
Keywords: HIF pathway; hybrid sturgeon; hypoxia; hypoxia-induced factor; physiological response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The physiological performance and immune responses of juvenile Amur sturgeon (Acipenser schrenckii) to stocking density and hypoxia stress.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014 Feb;36(2):325-35. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2013.12.002. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24355406
-
Exposure of Persian sturgeon (Acipenser persicus) to cadmium results in biochemical, histological and transcriptional alterations.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016 Mar-Apr;181-182:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2015.12.004. Epub 2015 Dec 11. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26687766
-
Identification of Hybrid Sturgeon (Acipenser baerii × Acipenser schrenckii) from Their Parents Using Germplasm.Animals (Basel). 2025 Mar 21;15(7):907. doi: 10.3390/ani15070907. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40218301 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive and maladaptive cardiorespiratory responses to continuous and intermittent hypoxia mediated by hypoxia-inducible factors 1 and 2.Physiol Rev. 2012 Jul;92(3):967-1003. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00030.2011. Physiol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22811423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia-inducible transcription factors in fish: expression, function and interconnection with the circadian clock.J Exp Biol. 2018 Jul 4;221(Pt 13):jeb163709. doi: 10.1242/jeb.163709. J Exp Biol. 2018. PMID: 29973414 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating the impact of camel whey protein hydrolysate on cyp1a1 and keap1/nrf2 expression in hypoxic stress-affected liver tissue of Oreochromis niloticus.J Comp Physiol B. 2025 Jun;195(3):323-338. doi: 10.1007/s00360-025-01623-2. Epub 2025 Jun 10. J Comp Physiol B. 2025. PMID: 40493086
-
Transcriptome analysis reveals hypoxic response key genes and modules as well as adaptive mechanism of crucian carp (Carassius auratus) gill under hypoxic stress.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 5;16:1543605. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1543605. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39975546 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial for the "Genetic Studies of Fish" Special Issue.Genes (Basel). 2025 Jun 27;16(7):752. doi: 10.3390/genes16070752. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40725408 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang D., Lu T.Y., Liu H.B. Characterization and Genetic Diversity of the Sturgeon Acipenser Schrenskil Ig Heavy Chain. Immunobiology. 2009;214:359–366. - PubMed
-
- Xu G.L., Xing W., Li T.L., Ma Z.H., Liu C.L., Jiang N., Luo L. Effects of Dietary Raffinose on Growth, Non-Specific Immunity, Intestinal Morphology and Microbiome of Juvenile Hybrid Sturgeon (Acipenser Baeri Brandt ♀ × A. Schrenckii Brandt ♂) Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018;72:237–246. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2017.11.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wei Q., He J., Yang D., Zheng W., Li L. Status of Sturgeon Aquaculture and Sturgeon Trade in China: A Review Based on Two Recent Nationwide Surveys. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2004;20:321–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0426.2004.00593.x. - DOI
-
- Williot P., Sabeau L., Gessner J., Arlati G., Bronzi P., Gulyas T., Berni P. Sturgeon Farming in Western Europe: Recent Developments and Perspectives. Aquat. Living Resour. 2001;14:367–374. doi: 10.1016/S0990-7440(01)01136-6. - DOI
-
- Guo Z., Zhu X., Liu J., Han D., Yang Y., Lan Z., Xie S. Effects of Dietary Protein Level on Growth Performance, Nitrogen and Energy Budget of Juvenile Hybrid Sturgeon, Acipenser Baerii ♀ × a. Gueldenstaedtii ♂. Aquaculture. 2012;338:89–95. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2012.01.008. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 6232041, 6222010/Beijing Natural Science Foundation
- 32002397/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- QNJJ202419/Youth Research Fund of Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences
- JJPY-2024-02/Reform and Development Project of Fisheries Science Institute, Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences
- CARS-46/The Earmarked Fund for CARS-46
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

