Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Solutions for Sustainable Food Packaging
- PMID: 38928343
- PMCID: PMC11203612
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25126638
Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Solutions for Sustainable Food Packaging
Abstract
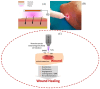
Increasing the number of resistant bacteria resistant to treatment is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. These bacteria are created in wounds and injuries and can be transferred through hospital equipment. Various attempts have been made to treat these bacteria in recent years, such as using different drugs and new sterilization methods. However, some bacteria resist drugs, and other traditional methods cannot destroy them. In the meantime, various studies have shown that cold atmospheric plasma can kill these bacteria through different mechanisms, making cold plasma a promising tool to deactivate bacteria. This new technology can be effectively used in the food industry because it has the potential to inactivate microorganisms such as spores and microbial toxins and increase the wettability and printability of polymers to pack fresh and dried food. It can also increase the shelf life of food without leaving any residue or chemical effluent. This paper investigates cold plasma's potential, advantages, and disadvantages in the food industry and sterilization.
Keywords: bacterial inactivation; cold atmospheric plasma; food packaging; sterilization.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Shelar A., Singh A.V., Dietrich P., Maharjan R.S., Thissen A., Didwal P.N., Shinde M., Laux P., Luch A., Mathe V. Emerging cold plasma treatment and machine learning prospects for seed priming: A step towards sustainable food production. RSC Adv. 2022;12:10467–10488. doi: 10.1039/D2RA00809B. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Koulik P., Begounov S., Goloviatinskii S. Atmospheric plasma sterilization and deodorization of dielectric surfaces. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 1999;19:311–326. doi: 10.1023/A:1021604027855. - DOI
-
- Boeckmann L., Schäfer M., Bernhardt T., Semmler M.L., Jung O., Ojak G., Fischer T., Peters K., Nebe B., Müller-Hilke B. Cold atmospheric pressure plasma in wound healing and cancer treatment. Appl. Sci. 2020;10:6898. doi: 10.3390/app10196898. - DOI
-
- Kotov D., Krivenchuk D., Osipov A., Patseev S., Aksiuchyts A., Ponomarenko G., Kulchitsky V. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Treatment of Medical Devices. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2019;22:16745–16749.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

