Comparative Nutritional and Histological Analysis of Malabar Red Snapper (Lutjanus malabaricus) and Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer)
- PMID: 38929422
- PMCID: PMC11200453
- DOI: 10.3390/ani14121803
Comparative Nutritional and Histological Analysis of Malabar Red Snapper (Lutjanus malabaricus) and Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer)
Abstract
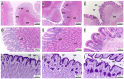
This study offers a comprehensive morpho-histological analysis of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) of the Malabar red snapper. A comparison of its GIT morphology with that of the Asian seabass reveals similarities and differences between the two species. Additionally, the moisture content, crude protein, and ash in the fillets of Malabar red snapper and Asian seabass were slightly different, with Malabar red snapper exhibiting higher levels of essential fatty acids. Furthermore, higher levels of the polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA)/saturated fatty acid (SFA) ratio and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)/eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) ratio, and a lower omega-6/omega-3 ratio, were observed in Malabar red snapper compared to Asian seabass. The Malabar red snapper's esophagus featured protective mechanisms such as simple columnar epithelial cells, mucous-secreting glands, and goblet cells that were predominantly stained for acid and neutral mucosubstances. Furthermore, its stomach, with mucus cells that were weakly stained for acid mucosubstances, exhibited distinct regions with varying glandular densities, with the pyloric region featuring few glands. The pyloric caeca of the fish were composed of five finger-like structures and few goblet cells. Several goblet cells gradually increased from the anterior to the posterior region of the intestine. These findings provide useful insights for the aquaculture sector, focusing on Malabar red snapper.
Keywords: Malabar red snapper; fillet fatty acids; gastrointestinal micromorphology; goblet cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The co-author (M.V.) is an employee of a company that partially financed the project. The other author has no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- FAO . The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022. Towards Blue Transformation. FAO; Rome, Italy: 2022. - DOI
-
- Vij S., Kuhl H., Kuznetsova I.S., Komissarov A., Yurchenko A.A., Van Heusden P., Singh S., Thevasagayam N.M., Prakki S.R., Purushothaman K., et al. Chromosomal-level assembly of the Asian Seabass genome using long sequence reads and multi-layered scaffolding. PLoS Genet. 2016;12:e1005954. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005954. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vij S., Purushothaman K., Gopikrishna G., Lau D., Saju J.M., Shamsudheen K.V., Kumar K.V., Basheer V.S., Gopalakrishnan A., Hossain M.S., et al. Barcoding of Asian seabass across its geographic range provides evidence for its bifurcation into two distinct species. Front. Mar. Sci. 2014;1:30. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2014.00030. - DOI
-
- Safiin N.S.Z., Ching F.F., Shapawi R. Successful co-feeding of Asian Seabass, Lates calcarifer larvae with palm oil-based microdiets and live feeds. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022;6:836275. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2022.836275. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

