Manual Therapy of Dysphagia in a Patient with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Case Report
- PMID: 38929462
- PMCID: PMC11205607
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina60060845
Manual Therapy of Dysphagia in a Patient with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Case Report
Abstract
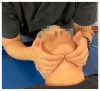
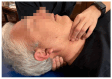
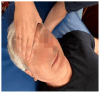
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is an incurable rare neurodegenerative condition, with 45% of cases showing the symptom of dysphagia; its clinical signs are atrophy, weakness, and fasciculations of the facial muscles, tongue, and pharynx. Furthermore, dysphagia is the main cause of aspiration pneumonia. The traditional treatment for dysphagia varies based on the patient's difficulty of swallowing. The initial phase consists of dietary consistency adjustments, progressing to alternatives like nasogastric tubes or percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) in advanced stages. Osteopathic manipulative treatment (OMT) is a complementary 'hands-on' approach that has already shown positive results as an add-on therapy in various health conditions. This study is a case report of a man diagnosed with ALS with initial dysphagia, managed with a protocol that extraordinarily included OMT. The patient showed somatic dysfunctions in the mediastinal region, upper cervical region, and occipital area which are all anatomically related to the nervous system, especially the glossopharyngeal reflex. At the end of the rehabilitation protocol, there was a reduction in the swallowing problems measured with Strand Scale and swallowing tests, and the patient reported an improved psycho-physical well-being assessed with the Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Assessment Questionnaire (ALSAQ-40). Instead, the neurological function measured with ALSFRS-S remained stable. Although the nature of this study design prevents any causal assumption, the positive results should lead to future randomized controlled trials to assess the effectiveness of OMT as an adjunctive therapeutic proposal to improve the health of ALS patients.
Keywords: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS); central nervous system; dysphagia; osteopathic manipulative treatment (OMT); osteopathic medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tongue strength, dysphagia questionnaire, pharyngeal secretions and FEES findings in dysphagia management in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2021 Aug;48(4):672-682. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2020.10.007. Epub 2020 Oct 24. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2021. PMID: 33109427
-
Nutrition with Gastrostomy Feeding Tubes for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis in Canada.Can J Neurol Sci. 2016 Nov;43(6):796-800. doi: 10.1017/cjn.2016.28. Epub 2016 Apr 4. Can J Neurol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27039940
-
Narrative review of diagnosis, management and treatment of dysphagia and sialorrhea in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.J Neurol. 2024 Oct;271(10):6508-6513. doi: 10.1007/s00415-024-12657-x. Epub 2024 Aug 29. J Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39207520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysphagia in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Relationships between disease progression and Fiberoptic Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2017 Jun;44(3):306-312. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2016.07.002. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2017. PMID: 27569290
-
[Dysphagia in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis--the mechanism and managements].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1995 Dec;35(12):1557-9. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1995. PMID: 8752462 Review. Japanese.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous