Overweight, Obesity, and Associated Risk Factors among Students at the Faculty of Medicine, Jazan University
- PMID: 38929557
- PMCID: PMC11206014
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina60060940
Overweight, Obesity, and Associated Risk Factors among Students at the Faculty of Medicine, Jazan University
Abstract
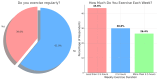
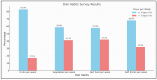
Background and Objectives: This study aimed to determine the prevalence of overweight, obesity, and the associated risk factors among medical students at Jazan University in Saudi Arabia. Materials and Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted among 228 medical students from their second to sixth academic years at the Faculty of Medicine, Jazan University. A self-administered questionnaire was used to collect data regarding sociodemographic characteristics, physical activity, dietary habits, comorbidities, medication use, family history, and lifestyle factors. Anthropometric measurements including height, weight, and waist circumference were recorded. Chi-square test and binary logistic regression were used to identify the risk factors associated with obesity. Results: The prevalence of overweight and obesity among the participants was 13.3% and 15%, respectively. Hence, the combined prevalence of overweight and obesity is 28.3%. The mean weight was 63.39 ± 18.93 kg, and the mean height was 163.48 ± 9.78 cm. On the other hand, 17.3% of participants were underweight, whereas 54.4% had normal BMI. Most of the participants (61%) did not engage in regular exercise. A high proportion consumed fruits (82.9%) and vegetables (58.8%) 3 or fewer days per week, and 84.2% consumed 3 or fewer meals per day. Fast-food consumption more than 3 days per week was reported by 42.1% of participants. Obesity was not significantly associated with sociodemographic factors, physical activity, dietary habits, comorbidities, medication use, or family histories. However, those with a monthly family income of SAR 15,000-24,999 had significantly lower odds of obesity than those in the lowest income group (OR 0.230, p = 0.045). Conclusions: The prevalence of overweight and obesity among medical students at Jazan University is high. Although no significant associations were found between obesity and most risk factors, this study highlights the need for interventions that promote healthy lifestyles among medical students. Further research is needed to identify effective strategies for preventing and managing obesity in this population.
Keywords: Jazan University; dietary habits; medical students; obesity; overweight; physical activity; prevalence; risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Obesity and Overweight. [(accessed on 28 March 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
-
- Defining Adult Overweight & Obesity|Overweight & Obesity|CDC. [(accessed on 28 March 2024)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/basics/adult-defining.html.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous