Improving IVF Utilization with Patient-Centric Artificial Intelligence-Machine Learning (AI/ML): A Retrospective Multicenter Experience
- PMID: 38930089
- PMCID: PMC11204457
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13123560
Improving IVF Utilization with Patient-Centric Artificial Intelligence-Machine Learning (AI/ML): A Retrospective Multicenter Experience
Abstract
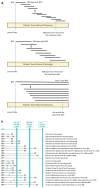
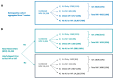
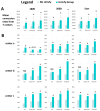
Objectives: In vitro fertilization (IVF) has the potential to give babies to millions more people globally, yet it continues to be underutilized. We established a globally applicable and locally adaptable IVF prognostics report and framework to support patient-provider counseling and enable validated, data-driven treatment decisions. This study investigates the IVF utilization rates associated with the usage of machine learning, center-specific (MLCS) prognostic reports (the Univfy® report) in provider-patient pre-treatment and IVF counseling. Methods: We used a retrospective cohort comprising 24,238 patients with new patient visits (NPV) from 2016 to 2022 across seven fertility centers in 17 locations in seven US states and Ontario, Canada. We tested the association of Univfy report usage and first intra-uterine insemination (IUI) and/or first IVF usage (a.k.a. conversion) within 180 days, 360 days, and "Ever" of NPV as primary outcomes. Results: Univfy report usage was associated with higher direct IVF conversion (without prior IUI), with odds ratios (OR) 3.13 (95% CI 2.83, 3.46), 2.89 (95% CI 2.63, 3.17), and 2.04 (95% CI 1.90, 2.20) and total IVF conversion (with or without prior IUI), OR 3.41 (95% CI 3.09, 3.75), 3.81 (95% CI 3.49, 4.16), and 2.78 (95% CI 2.59, 2.98) in 180-day, 360-day, and Ever analyses, respectively; p < 0.05. Among patients with Univfy report usage, after accounting for center as a factor, older age was a small yet independent predictor of IVF conversion. Conclusions: Usage of a patient-centric, MLCS-based prognostics report was associated with increased IVF conversion among new fertility patients. Further research to study factors influencing treatment decision making and real-world optimization of patient-centric workflows utilizing the MLCS reports is warranted.
Keywords: AI/ML; IVF; IVF access; IVF conversion; IVF outcomes; IVF utilization; artificial intelligence (AI); fertility; fertility access; live birth outcomes; machine learning (ML); prediction model; prognostics tool.
Conflict of interest statement
M. Yao, E.T. Nguyen, T. Swanson, and X. Chen report employment by and receipt of stock options from Univfy Inc. during the time period when the research was conducted. M. Yao reports being board director and shareholder of Univfy Inc., and she is also an inventor or co-inventor on Univfy Inc.’s issued and pending patents. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE), 2022 ART Factsheet. [(accessed on 29 April 2024)]. Available online: https://www.eshre.eu/Press-Room/Resources.
-
- Human Fertilisation & Embryology Authority (HFEA), 2019 Multiple Births in Fertility Treatment 2019. [(accessed on 29 April 2024)]; Available online: https://www.hfea.gov.uk/about-us/publications/research-and-data/multiple....
-
- International Committee Monitoring Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ICMART), 2018 ICMART Preliminary World Report 2018. [(accessed on 29 April 2024)]. Available online: https://www.icmartivf.org/reports-publications/#articles.
-
- Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology (SART), 2022 More Than 73 Thousand Babies Born from Assisted Reproductive Technology Cycles Done in 2020. [(accessed on 29 April 2024)]. Available online: https://www.sart.org/news-and-publications/news-and-research/press-relea...
-
- World Health Organization (WHO), 2023 1 in 6 People Globally Affected by Infertility: WHO. [(accessed on 29 April 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/04-04-2023-1-in-6-people-globally-affected....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

