The Identification and Evaluation of Interleukin-7 as a Myokine Biomarker for Peripheral Artery Disease Prognosis
- PMID: 38930112
- PMCID: PMC11205196
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13123583
The Identification and Evaluation of Interleukin-7 as a Myokine Biomarker for Peripheral Artery Disease Prognosis
Abstract
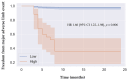
Background/Objectives: Myokines have been demonstrated to be associated with cardiovascular diseases; however, they have not been studied as biomarkers for peripheral artery disease (PAD). We identified interleukin-7 (IL-7) as a prognostic biomarker for PAD from a panel of myokines and developed predictive models for 2-year major adverse limb events (MALEs) using clinical features and plasma IL-7 levels. Methods: A prognostic study was conducted with a cohort of 476 patients (312 with PAD and 164 without PAD) that were recruited prospectively. Their plasma concentrations of five circulating myokines were measured at recruitment, and the patients were followed for two years. The outcome of interest was two-year MALEs (composite of major amputation, vascular intervention, or acute limb ischemia). Cox proportional hazards analysis was performed to identify IL-7 as the only myokine that was associated with 2-year MALEs. The data were randomly divided into training (70%) and test sets (30%). A random forest model was trained using clinical characteristics (demographics, comorbidities, and medications) and plasma IL-7 levels with 10-fold cross-validation. The primary model evaluation metric was the F1 score. The prognostic model was used to classify patients into low vs. high risk of developing adverse limb events based on the Youden Index. Freedom from MALEs over 2 years was compared between the risk-stratified groups using Cox proportional hazards analysis. Results: Two-year MALEs occurred in 28 (9%) of patients with PAD. IL-7 was the only myokine that was statistically significantly correlated with two-year MALE (HR 1.56 [95% CI 1.12-1.88], p = 0.007). For the prognosis of 2-year MALEs, our model achieved an F1 score of 0.829 using plasma IL-7 levels in combination with clinical features. Patients classified as high-risk by the predictive model were significantly more likely to develop MALEs over a 2-year period (HR 1.66 [95% CI 1.22-1.98], p = 0.006). Conclusions: From a panel of myokines, IL-7 was identified as a prognostic biomarker for PAD. Using a combination of clinical characteristics and plasma IL-7 levels, we propose an accurate predictive model for 2-year MALEs in patients with PAD. Our model may support PAD risk stratification, guiding clinical decisions on additional vascular evaluation, specialist referrals, and medical/surgical management, thereby improving outcomes.
Keywords: interleukin-7; myokines; peripheral artery disease; predictive model; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Investigating the Prognostic Potential of Plasma ST2 in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease: Identification and Evaluation.Proteomes. 2024 Aug 29;12(3):24. doi: 10.3390/proteomes12030024. Proteomes. 2024. PMID: 39311197 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Peripheral Artery Disease Prognosis Using Clinical and Inflammatory Biomarker Data.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Jul 22;17:4865-4879. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S471150. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39070129 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Evaluation of Angiogenesis-Related Proteins That Predict Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024 Dec 13;11(12):402. doi: 10.3390/jcdd11120402. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024. PMID: 39728292 Free PMC article.
-
Development and evaluation of a prediction model for peripheral artery disease-related major adverse limb events using novel biomarker data.J Vasc Surg. 2024 Aug;80(2):490-497.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2024.03.450. Epub 2024 Apr 8. J Vasc Surg. 2024. PMID: 38599293
-
Current Prognostic Biomarkers for Peripheral Arterial Disease: A Comprehensive Systematic Review of the Literature.Metabolites. 2025 Mar 25;15(4):224. doi: 10.3390/metabo15040224. Metabolites. 2025. PMID: 40278353 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stabilization Splint Therapy for Patients with Temporomandibular Disorders Improves Opening Movements and Jaw Limitation and Attenuates Pain by Influencing the Levels of IL-7, IL-8, and IL-13 in the Gingival Crevicular Fluid.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Feb 21;61(3):375. doi: 10.3390/medicina61030375. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40142185 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Major Adverse Limb Events in Females with Peripheral Artery Disease using Blood-Based Biomarkers and Clinical Features.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2025 Apr;18(2):316-330. doi: 10.1007/s12265-024-10574-y. Epub 2024 Dec 6. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 39643751
-
Evidence of Inflammatory Network Disruption in Chronic Venous Disease: An Analysis of Circulating Cytokines and Chemokines.Biomedicines. 2025 Jan 9;13(1):150. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13010150. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 39857734 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon Gamma and Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Are Inflammatory Biomarkers for Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease.Biomedicines. 2025 Jun 29;13(7):1586. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13071586. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40722661 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Prognostic Potential of Plasma ST2 in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease: Identification and Evaluation.Proteomes. 2024 Aug 29;12(3):24. doi: 10.3390/proteomes12030024. Proteomes. 2024. PMID: 39311197 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zemaitis M.R., Boll J.M., Dreyer M.A. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2021. Peripheral Arterial Disease. - PubMed
-
- Mehta A., Dhindsa D.S., Hooda A., Nayak A., Massad C.S., Rao B., Makue L.F., Rajani R.R., Alabi O., Quyyumi A.A., et al. Premature Atherosclerotic Peripheral Artery Disease: An Underrecognized and Undertreated Disorder with a Rising Global Prevalence. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2021;31:351–358. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2020.06.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zamzam A., Syed M.H., Rotstein O.D., Eikelboom J., Klein D.J., Singh K.K., Abdin R., Qadura M. Validating Fatty Acid Binding Protein 3 as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Peripheral Arterial Disease: A Three-Year Prospective Follow-up Study. EClinicalMedicine. 2023;55:101766. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101766. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

