The Effect of Obesity on Repolarization and Other ECG Parameters
- PMID: 38930116
- PMCID: PMC11205044
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13123587
The Effect of Obesity on Repolarization and Other ECG Parameters
Abstract
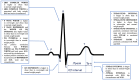
Background: Overweight and obesity are important risk factors in the development of cardiovascular diseases. New repolarization markers, such as the Tpeak-Tend interval and JTpeak intervals, have not yet been profoundly studied in obese patients. The study aims to analyze whether, in patients with obesity and overweight, repolarization markers, including the Tpeak-Tend interval, are prolonged and simultaneously check the frequency of other ECG pathologies in a 12-lead ECG in this group of patients. Methods: A study group consisted of 181 adults (90 females and 91 males) with overweight and first-class obesity. The participants completed a questionnaire, and the ECG was performed and analyzed. Results: When analyzing the classic markers, only QT dispersion was significantly higher in obese people. The Tpeak-Tend parameter (97.08 ms ± 23.38 vs. 89.74 ms ± 12.88, respectively), its dispersion, and JTpeak-JTend parameters were statistically significantly longer in the obese group than in the controls. There were also substantial differences in P-wave, QRS duration, and P-wave dispersion, which were the highest in obese people. Tpeak-Tend was positively correlated with body mass and waist circumference, while JTpeak was with BMI, hip circumference, and WHR. Tpeak/JT was positively correlated with WHR and BMI. In backward stepwise multiple regression analysis for JTpeak-WHR, type 2 diabetes and smoking had the highest statistical significance. Conclusions: Only selected repolarization markers are significantly prolonged in patients with class 1 obesity and, additionally, in this group, we identified more pathologies of P wave as well as prolonged QRS duration.
Keywords: electrocardiography; obesity; overweight; repolarization markers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization Obesity and Overweight. [(accessed on 12 August 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
-
- Global Health Estimates: Leading Causes of Death. [(accessed on 12 August 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/mortality-and-global-health-est....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources