Reliability of the AI-Assisted Assessment of the Proximity of the Root Apices to Mandibular Canal
- PMID: 38930132
- PMCID: PMC11204399
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13123605
Reliability of the AI-Assisted Assessment of the Proximity of the Root Apices to Mandibular Canal
Abstract
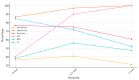
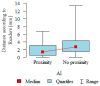
Background: This study evaluates the diagnostic accuracy of an AI-assisted tool in assessing the proximity of the mandibular canal (MC) to the root apices (RAs) of mandibular teeth using computed tomography (CT). Methods: This study involved 57 patients aged 18-30 whose CT scans were analyzed by both AI and human experts. The primary aim was to measure the closest distance between the MC and RAs and to assess the AI tool's diagnostic performance. The results indicated significant variability in RA-MC distances, with third molars showing the smallest mean distances and first molars the greatest. Diagnostic accuracy metrics for the AI tool were assessed at three thresholds (0 mm, 0.5 mm, and 1 mm). Results: The AI demonstrated high specificity but generally low diagnostic accuracy, with the highest metrics at the 0.5 mm threshold with 40.91% sensitivity and 97.06% specificity. Conclusions: This study underscores the limited potential of tested AI programs in reducing iatrogenic damage to the inferior alveolar nerve (IAN) during dental procedures. Significant differences in RA-MC distances between evaluated teeth were found.
Keywords: artificial intelligence (AI); automatic detection; computed tomography; dental imaging; diagnostic test accuracy; mandibular canal; root apex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Assessing the accuracy of artificial intelligence in mandibular canal segmentation compared to semi-automatic segmentation on cone-beam computed tomography images.Pol J Radiol. 2025 Apr 10;90:e172-e179. doi: 10.5114/pjr/202477. eCollection 2025. Pol J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40416521 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation the Relationship between Mandibular Molar Root Apices and Mandibular Canal among Residents of the Moscow Population using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Technique.Contemp Clin Dent. 2022 Jan-Mar;13(1):3-8. doi: 10.4103/ccd.ccd_388_19. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Contemp Clin Dent. 2022. PMID: 35466297 Free PMC article.
-
Distance and Bone Density between the Root Apex and the Mandibular Canal: A Cone-beam Study of 9202 Roots from a Brazilian Population.J Endod. 2019 May;45(5):538-542.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2019.01.004. Epub 2019 Mar 23. J Endod. 2019. PMID: 30910355
-
The anatomical relationship between the roots of erupted permanent teeth and the mandibular canal: a systematic review.Surg Radiol Anat. 2020 May;42(5):529-542. doi: 10.1007/s00276-019-02404-7. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Surg Radiol Anat. 2020. PMID: 31900577
-
A cone-beam computed tomography study of the anatomical relationships between mandibular teeth and the mandibular canal, with a review of the current literature.Microsc Res Tech. 2018 Mar;81(3):308-314. doi: 10.1002/jemt.22980. Epub 2017 Dec 29. Microsc Res Tech. 2018. PMID: 29285826 Review.
Cited by
-
Concerns regarding deployment of AI-based applications in dentistry - a review.BDJ Open. 2025 Mar 25;11(1):27. doi: 10.1038/s41405-025-00319-7. BDJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40133287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the accuracy of artificial intelligence in mandibular canal segmentation compared to semi-automatic segmentation on cone-beam computed tomography images.Pol J Radiol. 2025 Apr 10;90:e172-e179. doi: 10.5114/pjr/202477. eCollection 2025. Pol J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40416521 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

