Effects of Micro- and Nanosilica on the Mechanical and Microstructural Characteristics of Some Special Mortars Made with Recycled Concrete Aggregates
- PMID: 38930161
- PMCID: PMC11204823
- DOI: 10.3390/ma17122791
Effects of Micro- and Nanosilica on the Mechanical and Microstructural Characteristics of Some Special Mortars Made with Recycled Concrete Aggregates
Abstract
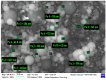
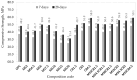
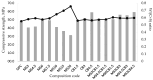
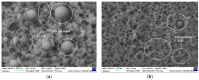
In this paper, we study the influence of densified microsilica and colloidal nanosilica admixtures on the mechanical strength and the microstructural characteristics of special mortars used for immobilizing radioactive concrete waste. The experimental program focused on the replacement of cement with micro- and/or nanosilica, in different proportions, in the basic composition of a mortar made with recycled aggregates. The technical criteria imposed for such cementitious systems, used for the encapsulation of low-level radioactive waste, imply high fluidity, increased mechanical strength and lack of segregation and of bleeding. We aimed to increase the structural compactness of the mortars by adding micro- and nanosilica, all the while maintaining the technical criteria imposed, to obtain a cement matrix with high durability and increased capacity for immobilizing radionuclides. The samples from all the compositions obtained were analyzed from the point of view of mechanical strength. Also, micro- and nanosilica as well as samples of the optimal mortar compositions were analyzed physically and microstructurally. Experimental data showed that the mortar samples present maximum compressive strength for a content between 6 and 7.5% wt. of microsilica, respectively, for a content of 2.25% wt. nanosilica. The obtained results suggest a synergistic effect of micro- and nanosilica when they are used simultaneously in cementitious compositions. Thus, among the analyzed compositional variants, the mortar composition with 3% wt. microsilica and 2.25% wt. nanosilica showed the best performance, with an increase in compressive strength of 23.5% compared to the control sample (without micro- and nanosilica). Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) analysis and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images highlighted the decrease in pore diameter and the increase in structural compactness, especially for mortar samples with nanosilica content or a mixture of micro- and nanosilica. This study is useful in the field of recycling radioactive concrete resulting from the decommissioning of nuclear research or nuclear power reactors.
Keywords: colloidal nanosilica; microsilica; microstructure; physical–mechanical properties; recycled concrete aggregates; special mortars.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Utilization of agricultural, industrial waste and nanosilica as replacement for cementitious material and natural aggregates - Mechanical, microstructural and durability characteristics assessment.Environ Res. 2023 Aug 15;231(Pt 1):116010. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.116010. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 37119840
-
Study on the Influence of Nanosilica Sol on the Hydration Process of Different Kinds of Cement and Mortar Properties.Materials (Basel). 2021 Jun 30;14(13):3653. doi: 10.3390/ma14133653. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34208984 Free PMC article.
-
Recycled Mortars with Ceramic Aggregates. Pore Network Transmutation and Its Relationship with Physical and Mechanical Properties.Materials (Basel). 2021 Mar 21;14(6):1543. doi: 10.3390/ma14061543. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33801138 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Rock Dust Additives as Fine Aggregate Replacement on Properties of Cement Composites-A Review.Materials (Basel). 2022 Apr 18;15(8):2947. doi: 10.3390/ma15082947. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35454638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utilization of Recycled Brick Powder as Supplementary Cementitious Materials-A Comprehensive Review.Materials (Basel). 2024 Jan 28;17(3):637. doi: 10.3390/ma17030637. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38591483 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of Mineral Additives on Strength Properties of Standard Mortar.Materials (Basel). 2024 Aug 22;17(16):4158. doi: 10.3390/ma17164158. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39203336 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Mineral Additives on Aggregate Reactivity.Materials (Basel). 2024 Dec 24;18(1):7. doi: 10.3390/ma18010007. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39795654 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Snellings R., Scrivener K. Rapid screening tests for supplementary cementitious materials: Past and future. Mater. Struct. 2016;49:1219–1236. doi: 10.1617/s11527-015-0718-z. - DOI
-
- Qing Y., Zean Z., Deyu K., Rongshen C. Influence of nano-SiO2 addition on properties of hardened cement paste as compared with silica fume. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007;21:539–545. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2005.09.001. - DOI
-
- Abhilash P.P., Nayak D.K., Sangoju B., Kumar R., Kumvar V. Effect of nano-silica in concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021;278:347.
-
- Aly M., Hashmi M.S.J., Olabi A.G., Messeiry M., Abadir E.F., Hussain A.I. Effect of colloidal nano-silica on the mechanical and physical behavior of waste-glass cement mortar. Mater. Des. 2012;33:127–135. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2011.07.008. - DOI
-
- Ji T. Preliminary Study on the Water Permeability and Microstructure of Concrete Incorporating Nano-SiO2. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005;35:1943–1947. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2005.07.004. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

