Curvature-Insensitive Transparent Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Substrate Based on Large-Area Ag Nanoparticle-Coated Wrinkled Polystyrene/Polydimethylsiloxane Film for Reliable In Situ Detection
- PMID: 38931008
- PMCID: PMC11206736
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29122946
Curvature-Insensitive Transparent Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Substrate Based on Large-Area Ag Nanoparticle-Coated Wrinkled Polystyrene/Polydimethylsiloxane Film for Reliable In Situ Detection
Abstract
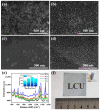
Flexible and transparent surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrates have attracted considerable attention for their ability to enable the direct in situ detection of analytes on curved surfaces. However, the curvature of an object can impact the signal enhancement of SERS during the measurement process. Herein, we propose a simple approach for fabricating a curvature-insensitive transparent SERS substrate by depositing silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) onto a large-area wrinkled polystyrene/polydimethylsiloxane (Ag NP@W-PS/PDMS) bilayer film. Using rhodamine 6G (R6G) as a probe molecule, the optimized Ag NP@W-PS/PDMS film demonstrates a high analytical enhancement factor (AEF) of 4.83 × 105, excellent uniformity (RSD = 7.85%) and reproducibility (RSD = 3.09%), as well as superior mechanical flexibility. Additionally, in situ measurements of malachite green (MG) on objects with diverse curvatures, including fish, apple, and blueberry, are conducted using a portable Raman system, revealing a consistent SERS enhancement. Furthermore, a robust linear relationship (R2 ≥ 0.990) between Raman intensity and the logarithmic concentration of MG detected from these objects is achieved. These results demonstrate the tremendous potential of the developed curvature-insensitive SERS substrate as a point-of-care testing (POCT) platform for identifying analytes on irregular objects.
Keywords: Ag NP-coated wrinkled PS/PDMS film; SERS; curvature insensitivity; point-of-care testing; quantitative detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Zhang D., Pu H., Huang L., Sun D. Advances in flexible surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrates for nondestructive food detection: Fundamentals and recent applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021;109:690–701. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2021.01.058. - DOI
-
- He X., Zhou X., Liu Y., Wang X. Ultrasensitive, recyclable and portable microfluidic surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) biosensor for uranyl ions detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020;311:127676. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2020.127676. - DOI
-
- Sun H., Li X., Hu Z., Gu C., Chen D., Wang J., Li B., Jiang T., Zhou X. Hydrophilic–hydrophobic silver nanowire paper based SERS substrate for in-situ detection of furazolidone under various environments. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021;556:149748. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149748. - DOI
-
- Tang S., Liu H., Tian Y., Chen D., Gu C., Wei G., Jiang T., Zhou J. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based lateral flow immunoassay mediated by hydrophilic–hydrophobic Ag-modified PMMA substrate. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021;262:120092. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2021.120092. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

