Acute and Repeated Ashwagandha Supplementation Improves Markers of Cognitive Function and Mood
- PMID: 38931168
- PMCID: PMC11207027
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16121813
Acute and Repeated Ashwagandha Supplementation Improves Markers of Cognitive Function and Mood
Abstract
Background: Ashwagandha has been reported to reduce stress and attenuate cognitive decline associated with inflammation and neurodegeneration in clinical populations. However, the effects as a potential nootropic nutrient in younger populations are unclear. This study examined the effects of liposomal ashwagandha supplementation on cognitive function, mood, and markers of health and safety in healthy young men and women.
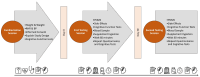
Methods: 59 men and women (22.7 ± 7 yrs., 74.9 ± 16 kg, 26.2 ± 5 BMI) fasted for 12 h, donated a fasting blood sample, and were administered the COMPASS cognitive function test battery (Word Recall, Word recognition, Choice Reaction Time Task, Picture Recognition, Digit Vigilance Task, Corsi Block test, Stroop test) and profile of mood states (POMS). In a randomized and double-blind manner, participants were administered 225 mg of a placebo (Gum Arabic) or ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) root and leaf extract coated with a liposomal covering. After 60-min, participants repeated cognitive assessments. Participants continued supplementation (225 mg/d) for 30 days and then returned to the lab to repeat the experiment. Data were analyzed using a general linear model (GLM) univariate analysis with repeated measures and pairwise comparisons of mean changes from baseline with 95% confidence intervals (CI).
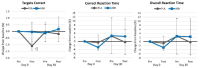
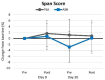
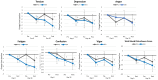
Results: Ashwagandha supplementation improved acute and/or 30-day measures of Word Recall (correct and recalled attempts), Choice Reaction Time (targets identified), Picture Recognition ("yes" correct responses, correct and overall reaction time), Digit Vigilance (correct reaction time), Stroop Color-Word (congruent words identified, reaction time), and POMS (tension and fatigue) from baseline more consistently with several differences observed between groups.
Conclusion: Results support contentions that ashwagandha supplementation (225 mg) may improve some measures of memory, attention, vigilance, attention, and executive function while decreasing perceptions of tension and fatigue in younger healthy individuals. Retrospectively registered clinical trial ISRCTN58680760.
Keywords: attention; cognition; executive function; memory; mood; nootropic; vigilance.
Conflict of interest statement
R.J. and M.P. are principals and researchers affiliated with Increnovo. They were not involved in the data collection or analysis. R.B.K. served as Principal Investigator at the study location. He has conducted sponsored grants and contracts awarded to the universities with which he has been affiliated, received an honorarium for making scientific presentations, served as an expert on legal cases, and consulted with industry on product development unrelated to the product studied. He has no financial or intellectual property-related conflict of interest with the study sponsor or nutrient examined. Other authors report no conflicts.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Effects of Supplementation with a Microalgae Extract from Phaeodactylum tricornutum Containing Fucoxanthin on Cognition and Markers of Health in Older Individuals with Perceptions of Cognitive Decline.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 5;16(17):2999. doi: 10.3390/nu16172999. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39275314 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Acute Ashwagandha Ingestion on Cognitive Function.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Sep 20;19(19):11852. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191911852. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36231152 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal) Root Extract in Improving Memory and Cognitive Functions.J Diet Suppl. 2017 Nov 2;14(6):599-612. doi: 10.1080/19390211.2017.1284970. Epub 2017 Feb 21. J Diet Suppl. 2017. PMID: 28471731 Clinical Trial.
-
Acute Effects of a Polyphenol-Rich Leaf Extract of Mangifera indica L. (Zynamite) on Cognitive Function in Healthy Adults: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Study.Nutrients. 2020 Jul 23;12(8):2194. doi: 10.3390/nu12082194. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32717999 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of the clinical use of Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) to ameliorate cognitive dysfunction.Phytother Res. 2020 Mar;34(3):583-590. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6552. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Phytother Res. 2020. PMID: 31742775
Cited by
-
Impact of a Withania somnifera and Bacopa monnieri Formulation on SH-SY5Y Human Neuroblastoma Cells Metabolism Through NMR Metabolomic.Nutrients. 2024 Nov 28;16(23):4096. doi: 10.3390/nu16234096. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39683490 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Nutrients on Neurological Disorders.Nutrients. 2024 Nov 23;16(23):4016. doi: 10.3390/nu16234016. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39683410 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying Withanolides in Plasma: Pharmacokinetic Studies and Analytical Methods.Nutrients. 2024 Nov 8;16(22):3836. doi: 10.3390/nu16223836. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39599622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Root Extract of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) on Perception of Recovery and Muscle Strength in Female Athletes.Eur J Sport Sci. 2025 Mar;25(3):e12265. doi: 10.1002/ejsc.12265. Eur J Sport Sci. 2025. PMID: 39954269 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Improving Sleep Quality to Enhance Athletic Activity-The Role of Nutrition and Supplementation: A Mini-Short Review.Nutrients. 2025 May 24;17(11):1779. doi: 10.3390/nu17111779. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40507048 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akhgarjand C., Asoudeh F., Bagheri A., Kalantar Z., Vahabi Z., Shab-Bidar S., Rezvani H., Djafarian K. Does Ashwagandha supplementation have a beneficial effect on the management of anxiety and stress? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Phytother. Res. 2022;36:4115–4124. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7598. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

