Morphofunctional Assessment beyond Malnutrition: Fat Mass Assessment in Adult Patients with Phenylketonuria-Systematic Review
- PMID: 38931188
- PMCID: PMC11206948
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16121833
Morphofunctional Assessment beyond Malnutrition: Fat Mass Assessment in Adult Patients with Phenylketonuria-Systematic Review
Abstract
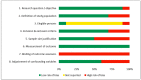
Morphofunctional assessment was developed to evaluate disease-related malnutrition. However, it can also be used to assess cardiometabolic risk, as excess adiposity increases this risk. Phenylketonuria (PKU) is the most prevalent inherited metabolic disease among adults, and obesity in PKU has recently gained interest, although fat mass correlates better with cardiometabolic risk than body mass index. In this systematic review, the objective was to assess whether adult patients with PKU have higher fat mass than healthy controls. Studies of adult PKU patients undergoing dietary treatment in a metabolic clinic reporting fat mass were included. The PubMed and EMBASE databases were searched. Relevance of articles, data collection, and risk of bias were evaluated by two independent reviewers. Ten articles were evaluated, six with a control group, including 310 subjects with PKU, 62 with mild hyperphenylalaninemia, and 157 controls. One study reported a significant and four a tendency towards an increased fat mass in all patients or only females with PKU. Limitations included not having a healthy control group, not reporting sex-specific results and using different techniques to assess fat mass. Evaluation of fat mass should be included in the morphofunctional assessment of cardiometabolic risk in adult patients with PKU.
Keywords: body composition; body fat; cardiovascular risk; metabolic diseases; morphofunctional assessment; phenylketonuria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Evaluating Therapy and Growth in Children with Phenylketonuria: A Retrospective Longitudinal Study from Two Romanian Centers.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Jul 22;60(7):1185. doi: 10.3390/medicina60071185. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39064614 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almeida J.M.G., García C.G., Castañeda V.B., Guerrero D.B. Nuevo enfoque de la nutrición. Valoración del estado nutricional del paciente: Función y composición corporal. Nutr. Hosp. 2018;35:1–14. doi: 10.20960/nh.2027. - DOI
-
- Rodrigues C., Pinto A., Faria A., Teixeira D., van Wegberg A.M.J., Ahring K., Feillet F., Calhau C., MacDonald A., Moreira-Rosário A., et al. Is the Phenylalanine-Restricted Diet a Risk Factor for Overweight or Obesity in Patients with Phenylketonuria (PKU)? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2021;13:3443. doi: 10.3390/nu13103443. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical