Dexamethasone-Induced Insulin Resistance Attenuation by Oral Sulfur-Oxidovanadium(IV) Complex Treatment in Mice
- PMID: 38931427
- PMCID: PMC11206843
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17060760
Dexamethasone-Induced Insulin Resistance Attenuation by Oral Sulfur-Oxidovanadium(IV) Complex Treatment in Mice
Abstract
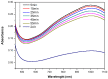
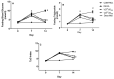
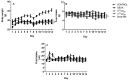
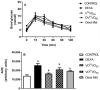
Vanadium compounds are known to exert insulin-enhancing activity, normalize elevated blood glucose levels in diabetic subjects, and show significant activity in models of insulin resistance (IR). Faced with insulin resistance, the present work investigates the antidiabetic performance of a known oxidovanadium(IV)-based coordination compound-[VIVO(octd)]-and effects associated with glucocorticoid-induced insulin resistance in mice. The effects of [VIVO(octd)] were evaluated in a female Swiss mice model of insulin resistance induced by seven days of dexamethasone treatment in comparison with groups receiving metformin treatment. Biological assays such as hematological, TyG index, hepatic lipids, glycogen, oxidative stress in the liver, and oral glucose tolerance tests were evaluated. [VIVO(octd)] was characterized with 51V NMR, infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR), electronic absorption spectroscopy, and mass spectrometry (ESI-FT-MS). The [VIVO(octd)] oral treatment (50 mg/kg) had an antioxidant effect, reducing 50% of fast blood glucose (p < 0.05) and 25% of the TyG index, which is used to estimate insulin resistance (p < 0.05), compared with the non-treated group. The oxidovanadium-sulfur compound is a promising antihyperglycemic therapeutic, including in cases aggravated by insulin resistance induced by glucocorticoid treatment.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; insulin resistance; vanadium complex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lima L.M.A., Murakami H., Gaebler D.J., Silva W.E., Belian M.F., Lira E.C., Crans D.C. Acute Toxicity Evaluation of Non-Innocent Oxidovanadium(V) Schiff Base Complex. Inorganics. 2021;9:42. doi: 10.3390/inorganics9060042. - DOI
-
- Nigro T.P., Manica G.C.M., Souza S.W., Jesus C.H.A., Bottini R.C.R., Missina J.M., Valdameri G., Nunes G.G., da Cunha J.M., Picheth G., et al. Heteroleptic oxidovanadium(IV)-malate complex improves glucose uptake in HepG2 and enhances insulin action in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Biometals. 2022;35:903–919. doi: 10.1007/s10534-022-00413-5. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

