Novel Protein Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets for Type 1 Diabetes and Its Complications: Insights from Summary-Data-Based Mendelian Randomization and Colocalization Analysis
- PMID: 38931433
- PMCID: PMC11206317
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17060766
Novel Protein Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets for Type 1 Diabetes and Its Complications: Insights from Summary-Data-Based Mendelian Randomization and Colocalization Analysis
Abstract
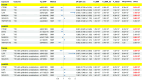
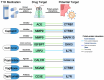
Millions of patients suffer from type 1 diabetes (T1D) and its associated complications. Nevertheless, the pursuit of a cure for T1D has encountered significant challenges, with a crucial impediment being the lack of biomarkers that can accurately predict the progression of T1D and reliable therapeutic targets for T1D. Hence, there is an urgent need to discover novel protein biomarkers and therapeutic targets, which holds promise for targeted therapy for T1D. In this study, we extracted summary-level data on 4907 plasma proteins from 35,559 Icelanders and 2923 plasma proteins from 54,219 UK participants as exposures. The genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary statistics on T1D and T1D with complications were obtained from the R9 release results from the FinnGen consortium. Summary-data-based Mendelian randomization (SMR) analysis was employed to evaluate the causal associations between the genetically predicted levels of plasma proteins and T1D-associated outcomes. Colocalization analysis was utilized to investigate the shared genetic variants between the exposure and outcome. Moreover, transcriptome analysis and a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network further illustrated the expression patterns of the identified protein targets and their interactions with the established targets of T1D. Finally, a Mendelian randomization phenome-wide association study evaluated the potential side effects of the identified core protein targets. In the primary SMR analysis, we identified 72 potential protein targets for T1D and its complications, and nine of them were considered crucial protein targets. Within the group were five risk targets and four protective targets. Backed by evidence from the colocalization analysis, the protein targets were classified into four tiers, with MANSC4, CTRB1, SIGLEC5 and MST1 being categorized as tier 1 targets. Delving into the DrugBank database, we retrieved 11 existing medications for T1D along with their therapeutic targets. The PPI network clarified the interactions among the identified potential protein targets and established ones. Finally, the Mendelian randomization phenome-wide association study corroborated MANSC4 as a reliable target capable of mitigating the risk of various forms of diabetes, and it revealed the absence of adverse effects linked to CTRB1, SIGLEC5 and MST1. This study unveiled many protein biomarkers and therapeutic targets for T1D and its complications. Such advancements hold great promise for the progression of drug development and targeted therapy for T1D.
Keywords: GWAS; Mendelian randomization; plasma proteins; therapeutic targets; type 1 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Proteome-Wide Mendelian Randomization and Colocalization Analysis Identify Therapeutic Targets for Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis.Biomolecules. 2024 Mar 15;14(3):355. doi: 10.3390/biom14030355. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38540773 Free PMC article.
-
PTGES2 and RNASET2 identified as novel potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for basal cell carcinoma: insights from proteome-wide mendelian randomization, colocalization, and MR-PheWAS analyses.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 5;15:1418560. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1418560. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39035989 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying new biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets for breast cancer through the integration of human plasma proteomics: a Mendelian randomization study and colocalization analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 16;15:1449668. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1449668. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39351539 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction and onset of type 2 diabetes along with its complications: a multi-omics Mendelian randomization and colocalization study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 30;15:1401531. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1401531. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39280009 Free PMC article.
-
Combining evidence from Mendelian randomization and colocalization: Review and comparison of approaches.Am J Hum Genet. 2022 May 5;109(5):767-782. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2022.04.001. Epub 2022 Apr 21. Am J Hum Genet. 2022. PMID: 35452592 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rib and Sternum Fractures From Falls: Global Burden of Disease and Predictions.Biomed Eng Comput Biol. 2025 Jun 27;16:11795972251350223. doi: 10.1177/11795972251350223. eCollection 2025. Biomed Eng Comput Biol. 2025. PMID: 40584268 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ogle G.D., James S., Dabelea D., Pihoker C., Svennson J., Maniam J., Klatman E.L., Patterson C.C. Global estimates of incidence of type 1 diabetes in children and adolescents: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Atlas, 10th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022;183:109083. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109083. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

