Pharmacokinetics, Dose-Proportionality, and Tolerability of Intravenous Tanespimycin (17-AAG) in Single and Multiple Doses in Dogs: A Potential Novel Treatment for Canine Visceral Leishmaniasis
- PMID: 38931434
- PMCID: PMC11206245
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17060767
Pharmacokinetics, Dose-Proportionality, and Tolerability of Intravenous Tanespimycin (17-AAG) in Single and Multiple Doses in Dogs: A Potential Novel Treatment for Canine Visceral Leishmaniasis
Abstract
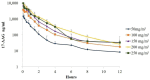
In the New World, dogs are considered the main reservoir of visceral leishmaniasis (VL). Due to inefficacies in existing treatments and the lack of an efficient vaccine, dog culling is one of the main strategies used to control disease, making the development of new therapeutic interventions mandatory. We previously showed that Tanespimycin (17-AAG), a Hsp90 inhibitor, demonstrated potential for use in leishmaniasis treatment. The present study aimed to test the safety of 17-AAG in dogs by evaluating plasma pharmacokinetics, dose-proportionality, and the tolerability of 17-AAG in response to a dose-escalation protocol and multiple administrations at a single dose in healthy dogs. Two protocols were used: Study A: four dogs received variable intravenous (IV) doses (50, 100, 150, 200, or 250 mg/m2) of 17-AAG or a placebo (n = 4/dose level), using a cross-over design with a 7-day "wash-out" period; Study B: nine dogs received three IV doses of 150 mg/m2 of 17-AAG administered at 48 h intervals. 17-AAG concentrations were determined by a validated high-performance liquid chromatographic (HPLC) method: linearity (R2 = 0.9964), intra-day precision with a coefficient of variation (CV) ≤ 8%, inter-day precision (CV ≤ 20%), and detection and quantification limits of 12.5 and 25 ng/mL, respectively. In Study A, 17-AAG was generally well tolerated. However, increased levels of liver enzymes-alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT)-and bloody diarrhea were observed in all four dogs receiving the highest dosage of 250 mg/m2. After single doses of 17-AAG (50-250 mg/m2), maximum plasma concentrations (Cmax) ranged between 1405 ± 686 and 9439 ± 991 ng/mL, and the area under the curve (AUC) plotting plasma concentration against time ranged between 1483 ± 694 and 11,902 ± 1962 AUC 0-8 h μg/mL × h, respectively. Cmax and AUC parameters were dose-proportionate between the 50 and 200 mg/m2 doses. Regarding Study B, 17-AAG was found to be well tolerated at multiple doses of 150 mg/m2. Increased levels of liver enzymes-ALT (28.57 ± 4.29 to 173.33 ± 49.56 U/L), AST (27.85 ± 3.80 to 248.20 ± 85.80 U/L), and GGT (1.60 ± 0.06 to 12.70 ± 0.50 U/L)-and bloody diarrhea were observed in only 3/9 of these dogs. After the administration of multiple doses, Cmax and AUC 0-48 h were 5254 ± 2784 μg/mL and 6850 ± 469 μg/mL × h in plasma and 736 ± 294 μg/mL and 7382 ± 1357 μg/mL × h in tissue transudate, respectively. In conclusion, our results demonstrate the potential of 17-AAG in the treatment of CVL, using a regimen of three doses at 150 mg/m2, since it presents the maintenance of high concentrations in subcutaneous interstitial fluid, low toxicity, and reversible hepatotoxicity.
Keywords: Tanespimycin (17-AAG); canine visceral leishmaniasis; dogs; dose-escalation protocol; pharmacokinetics; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of oral S-3304, a novel matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, in single and multiple dose escalation studies in healthy volunteers.Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005 Jun;43(6):282-93. doi: 10.5414/cpp43282. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005. PMID: 15968885 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of Bencycloquidium bromide, a novel selective muscarinic M1/M3 receptor antagonist, after single and multiple intranasal doses in healthy chinese subjects: an open-label, single-center, first-in-human study.Drugs R D. 2012 Mar 1;12(1):17-28. doi: 10.2165/11599330-000000000-00000. Drugs R D. 2012. PMID: 22339483 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase I, First-in-Human, Single and Multiple Ascending Dose- and Food-Effect Studies to Assess the Safety, Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics of a Novel Anti-hepatitis B Virus Drug, Bentysrepinine (Y101), in Healthy Chinese Subjects.Clin Drug Investig. 2020 Jun;40(6):555-566. doi: 10.1007/s40261-020-00909-3. Clin Drug Investig. 2020. PMID: 32277364 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetics of dexloxiglumide after administration of single and repeat oral escalating doses in healthy young males.Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2002 May;40(5):198-206. doi: 10.5414/cpp40198. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2002. PMID: 12051571 Clinical Trial.
-
Mitoxantrone: a review of its use in multiple sclerosis.CNS Drugs. 2004;18(6):379-96. doi: 10.2165/00023210-200418060-00010. CNS Drugs. 2004. PMID: 15089110 Review.
Cited by
-
Preliminary Pharmacokinetics and Appetite Stimulant Efficacy of Oral Mirtazapine in Guinea Pigs (Cavia porcellus).Animals (Basel). 2025 Jul 31;15(15):2256. doi: 10.3390/ani15152256. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40805046 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Teixeira-Neto R.G., Da Silva E.S., Nascimento R.A., Belo V.S., De Oliveira C.D.L., Pinheiro L.C., Gontijo C.M.F. Canine visceral leishmaniasis in an urban setting of Southeastern Brazil: An ecological study involving spatial analysis. Parasit. Vectors. 2014;7:485. doi: 10.1186/s13071-014-0485-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- França-Silva J.C., Barata R.A., Costa R.T., Monteiro E.M., Machado-Coelho G.L.L., Vieira E.P., Prata A., Mayrink W., Nascimento E., Fortes-Dias C.L., et al. Importance of Lutzomyia longipalpis in the dynamics of transmission of canine visceral leishmaniasis in the endemic area of Porteirinha Municipality, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2005;131:213–220. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2005.05.006. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

