Solubility, pH-Solubility Profile, pH-Rate Profile, and Kinetic Stability of the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, Alectinib
- PMID: 38931444
- PMCID: PMC11206852
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17060776
Solubility, pH-Solubility Profile, pH-Rate Profile, and Kinetic Stability of the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, Alectinib
Abstract
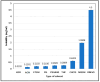
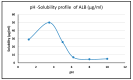
Alectinib HCl (ALBHCl) is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor used for non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). The aim of this study is to unlock some of the physicochemical properties of ALBHCL that serve as a database for any future studies. A solubility study of ALBHCL was performed in different solvents. Also, photostability was tested in the solution and solid states, and the order of reaction and rate constant were calculated. In addition to the pH solubility relation, the pH-rate relation at different temperatures was also studied, and the profiles were constructed. A solubility study was also performed in different media for the purpose of optimizing suitable sink conditions for the in vitro dissolution testing of solid dosage forms. Solubility tests in multiple solvents and pH conditions revealed that the highest solubility was in DMSO, methanol, and chloroform, with acidic media yielding the maximum solubility but degrading at rather low pH levels. ALBHCL proved unstable at high temperatures and under light exposure, with varying stability across different pH levels. The optimal dissolution media for in vitro oral dosage form evaluation were determined, achieving sink conditions at pH levels of 6.8 and 4.5 with specific additives. This study enhances the existing database on ALBHCL's physicochemical properties, emphasizing the importance of pH optimization in pharmaceutical processes and providing valuable insights into its pharmaceutical application.
Keywords: alectinib; non-small cell lung carcinoma; pH solubility; pH stability; photodegradation; solubility.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Solubility, Dissolution Rate, and Oral Bioavailability of β-Cyclodextrin and Hydroxypropyl β-Cyclodextrin as Inclusion Complexes of the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, Alectinib.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jun 5;17(6):737. doi: 10.3390/ph17060737. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38931404 Free PMC article.
-
Microenvironmental pH modulation in solid dosage forms.J Pharm Sci. 2007 May;96(5):948-59. doi: 10.1002/jps.20932. J Pharm Sci. 2007. PMID: 17455349 Review.
-
Investigation of solubility and dissolution of a free base and two different salt forms as a function of pH.Pharm Res. 2005 Apr;22(4):628-35. doi: 10.1007/s11095-005-2504-z. Epub 2005 Apr 7. Pharm Res. 2005. PMID: 15846471
-
Improving Dissolution Behavior and Oral Absorption of Drugs with pH-Dependent Solubility Using pH Modifiers: A Physiologically Realistic Mass Transport Analysis.Mol Pharm. 2021 Sep 6;18(9):3326-3341. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.1c00262. Epub 2021 Aug 24. Mol Pharm. 2021. PMID: 34428047
-
Salt formation to improve drug solubility.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007 Jul 30;59(7):603-16. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2007.05.010. Epub 2007 May 29. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007. PMID: 17619064 Review.
Cited by
-
Alectinib-Loaded Chitosan-Alginate Nanoparticles: A Novel Synthesis Method with In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluations.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Apr 8;17(4):492. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040492. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40284487 Free PMC article.
References
-
- [(accessed on 20 January 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cancer#tab=tab_1.
-
- Ettinger D.S., Wood D.E., Aisner D.L., Akerley W., Bauman J.R., Bharat A., Bruno D.S., Chang J.Y., Chirieac L.R., D’Amico T.A., et al. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 3.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2022;20:497–530. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2022.0025. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

