Phenolic Composition of Crataegus monogyna Jacq. Extract and Its Anti-Inflammatory, Hepatoprotective, and Antileukemia Effects
- PMID: 38931453
- PMCID: PMC11207108
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17060786
Phenolic Composition of Crataegus monogyna Jacq. Extract and Its Anti-Inflammatory, Hepatoprotective, and Antileukemia Effects
Abstract
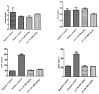
Crataegus monogyna (C. monogyna) is a prominent plant used in Moroccan traditional medicine. This study investigated the phenolic composition and the anti-inflammatory, the hepatoprotective, and the anticancer activities of a hydroethanolic extract of C. monogyna leaves and stems. Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography identified the phenolic profile. The in vitro anticancer activity was evaluated using the MTT assay on HL-60 and K-562 myeloleukemia cells and liver (Huh-7) cell lines. The anti-inflammatory effect was assessed in vivo using carrageenan-induced paw edema in rats. The hepatoprotective effect at 300 and 1000 mg/kg doses against the acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity on rats was studied for seven days. Additionally, molecular docking simulations were performed to evaluate the extract's inhibitory potential against key targets: lipoxygenase, cytochrome P450, tyrosine kinase, and TRADD. The extract exhibited significant cytotoxic activity against K-562 and HL-60 cells, but not against lung cancer cells (Huh-7 line). The 1000 mg/kg dose demonstrated the most potent anti-inflammatory effect, inhibiting edema by 99.10% after 6 h. C. monogyna extract displayed promising hepatoprotective properties. Procyanidin (-7.27 kcal/mol), quercetin (-8.102 kcal/mol), and catechin (-9.037 kcal/mol) were identified as the most active molecules against lipoxygenase, cytochrome P450, and tyrosine kinase, respectively. These findings highlight the untapped potential of C. monogyna for further exploration in treating liver damage, inflammation, and leukemia.
Keywords: Crataegus monogyna; hepatotoxicity; human hepatocellular carcinoma; in silico studies; inflammation; leukemia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Agour A., Mssillou I., Es-safi I., Conte R., Mechchate H., Slighoua M., Amrati F.E.-Z., Parvez M.K., Numan O., Bari A., et al. The Antioxidant, Analgesic, Anti-Inflammatory, and Wound Healing Activities of Haplophyllum Tuberculatum (Forsskal) A. Juss Aqueous and Ethanolic Extract. Life. 2022;12:1553. doi: 10.3390/life12101553. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amrati F.E.-Z., Chebaibi M., Galvão de Azevedo R., Conte R., Slighoua M., Mssillou I., Kiokias S., de Freitas Gomes A., Soares Pontes G., Bousta D. Phenolic Composition, Wound Healing, Antinociceptive, and Anticancer Effects of Caralluma Europaea Extracts. Molecules. 2023;28:1780. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041780. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Radi F.Z., Bencheikh N., Bouhrim M., Saleh A., Al kamaly O., Parvez M.K., Elbouzidi A., Bnouham M., Zair T. Phytochemical Analysis, Antioxidant, and Antihyperglycemic Activities of Crataegus Monogyna Jacq Aqueous Extract. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2023;18:1934578X231195157. doi: 10.1177/1934578X231195157. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

