Development and Optimization of Dipyridamole- and Roflumilast-Loaded Nanoemulsion and Nanoemulgel for Enhanced Skin Permeation: Formulation, Characterization, and In Vitro Assessment
- PMID: 38931470
- PMCID: PMC11207013
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17060803
Development and Optimization of Dipyridamole- and Roflumilast-Loaded Nanoemulsion and Nanoemulgel for Enhanced Skin Permeation: Formulation, Characterization, and In Vitro Assessment
Abstract
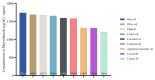
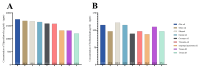
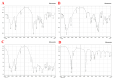
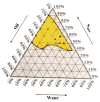
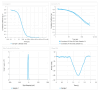
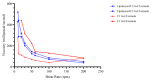
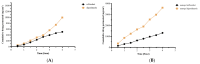
This study explores developing and optimizing a nanoemulsion (NE) system loaded with dipyridamole and roflumilast, aiming to improve skin penetration and retention. The NE formulation was further transformed into a nanoemulgel to enhance its application as a topical treatment for psoriasis. Solubility studies were conducted to select the oil, surfactant, and co-surfactant. Phase diagrams were constructed using the aqueous phase titration method. All the formulations were in nanoscale, and Formula (F2) (which contains oleic acid oil as the oil phase, a mixture of Surfactant Tween 80 and co-surfactant (ethanol) at a ratio of 1:2 in addition to distilled water as an aqueous phase in a ratio of 1:5:4, respectively) was the selected formula depending on the particle size, PDI, and zeta potential. Formula (F2) has the best ratio because it gives the smallest nanoemulsion globule size (particle size average of 167.1 nm), the best homogenicity (lowest PDI of 0.195), and the highest stability (higher zeta potential of -32.22). The selected formula was converted into a nanoemulgel by the addition of 0.5% (w/w) xanthan gum (average particle size of 172.7 nm) and the best homogenicity (lowest PDI of 0.121%) and highest stability (higher zeta potential of -28.31). In conclusion, the selected formula has accepted physical and chemical properties, which enhanced skin penetration.
Keywords: Franz cell diffusion; dipyridamole; nanoemulgel; nanoemulsion; psoriasis; roflumilast.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
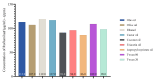

Similar articles
-
Topical Application of Dipyridamole and Roflumilast Combination Nanoparticles Loaded Nanoemulgel for the Treatment of Psoriasis in Rats.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Dec 7;19:13113-13134. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S492180. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39679247 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced transdermal permeability of piroxicam through novel nanoemulgel formulation.Int J Pharm Investig. 2014 Apr;4(2):65-76. doi: 10.4103/2230-973X.133053. Int J Pharm Investig. 2014. PMID: 25006551 Free PMC article.
-
Amelioration of Imiquimod-induced Psoriasis in the Mice model by Topical Delivery of Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitor Roflumilast Incorporated Nanoemulgel.Pharm Dev Technol. 2025 May 15:1-14. doi: 10.1080/10837450.2025.2505004. Online ahead of print. Pharm Dev Technol. 2025. PMID: 40372116
-
Co-Delivery of Imiquimod and Curcumin by Nanoemugel for Improved Topical Delivery and Reduced Psoriasis-Like Skin Lesions.Biomolecules. 2020 Jun 27;10(7):968. doi: 10.3390/biom10070968. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32605030 Free PMC article.
-
Nanogels as Potential Delivery Vehicles in Improving the Therapeutic Efficacy of Phytopharmaceuticals.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Oct 3;14(19):4141. doi: 10.3390/polym14194141. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36236089 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into the pharmaceutical properties of green fabricated Iron oxide nanoparticles.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 29;15(1):27621. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09327-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40730590 Free PMC article.
-
Topical Application of Dipyridamole and Roflumilast Combination Nanoparticles Loaded Nanoemulgel for the Treatment of Psoriasis in Rats.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Dec 7;19:13113-13134. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S492180. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39679247 Free PMC article.
-
The hepatoprotective effects of the polyphenol-enriched n-butanol fraction of Cnicus benedictus against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in rats: In vivo study.Toxicol Rep. 2024 Dec 5;14:101850. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2024.101850. eCollection 2025 Jun. Toxicol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39758800 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

