The Effectiveness of a Dietary Supplement with Honey, Propolis, Pelargonium sidoides Extract, and Zinc in Children Affected by Acute Tonsillopharyngitis: An Open, Randomized, and Controlled Trial
- PMID: 38931472
- PMCID: PMC11206353
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17060804
The Effectiveness of a Dietary Supplement with Honey, Propolis, Pelargonium sidoides Extract, and Zinc in Children Affected by Acute Tonsillopharyngitis: An Open, Randomized, and Controlled Trial
Abstract
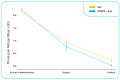
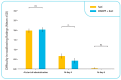
Physicians are currently finding products for pediatric respiratory diseases of viral etiology to reduce the inappropriate use of antibiotic therapy. This study evaluated PediaFlù (Pediatrica S.r.l.), a dietary supplement already on the market composed of honey, propolis, Pelargonium sidoides extract, and zinc (DSHPP), in children affected by acute tonsillopharyngitis (ATR). The open-label, randomized, and controlled study compared DSHPP + standard of care (SoC) versus SoC alone for six days. Children between 3 and 10 years with an ATR ≤ 48 h, a negative rapid test for beta-hemolytic Streptococcus, or a culture identification of nasal and/or pharyngeal exudates were included. A tonsillitis severity score (TSS) and the number of treatment failures (using ibuprofen or high-dose paracetamol as rescue medication) were the primary endpoints. DSHPP+ SoC showed better performance than SoC alone for TSS sub-scores: throat pain and erythema on day 6 (p < 0.001 and p < 0.05), swallowing (p < 0.01 on day 4), and TSS total score on days 4 and 6 (p < 0.05 and p < 0.001). Only one patient (SoC group) had treatment failure for ibuprofen administration. No adverse events were reported. DSHPP is an optimal adjuvant in the treatment of URTI and could potentially be useful in the daily clinical practice of paediatricians evaluating the correct antibiotic prescription.
Keywords: Pelargonium sidoides; dietary supplements; honey; nasopharyngitis; pharyngitis; propolis; severity score; tonsillitis; zinc.
Conflict of interest statement
D.F.B. is employed at Opera CRO, the contract research organization that managed the study. L.B. is employed at TIgermed Italy, the company that performed the data management of the study. V.M. is employed at Pediatrica S.r.l. F.C., S.R., and M.M.B. declare no conflicts of interest. The funder Pediatrica S.r.l., Livorno, Italy had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Open, Randomised, Controlled Study to Evaluate the Role of a Dietary Supplement Containing Pelargonium sidoides Extract, Honey, Propolis, and Zinc as Adjuvant Treatment in Children with Acute Tonsillopharyngitis.Children (Basel). 2025 Mar 10;12(3):345. doi: 10.3390/children12030345. Children (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150627 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of a Dietary Supplement (PediaFlù) Plus Standard of Care in Children With Acute Tonsillopharyngitis/Rhinopharyngitis: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial.JMIR Res Protoc. 2024 May 31;13:e53703. doi: 10.2196/53703. JMIR Res Protoc. 2024. PMID: 38819917 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of extract of Pelargonium sidoides in children with acute non-group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus tonsillopharyngitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Altern Ther Health Med. 2003 Sep-Oct;9(5):68-79. Altern Ther Health Med. 2003. PMID: 14526713 Clinical Trial.
-
Defining the optimum treatment regimen for azithromycin in acute tonsillopharyngitis.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004 Feb;23(2 Suppl):S129-34. doi: 10.1097/01.inf.0000112527.33870.0d. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004. PMID: 14770076 Review.
-
Faster recovery and reduced paracetamol use - a meta-analysis of EPs 7630 in children with acute respiratory tract infections.BMC Pediatr. 2019 Apr 23;19(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s12887-019-1473-z. BMC Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31014293 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Open, Randomised, Controlled Study to Evaluate the Role of a Dietary Supplement Containing Pelargonium sidoides Extract, Honey, Propolis, and Zinc as Adjuvant Treatment in Children with Acute Tonsillopharyngitis.Children (Basel). 2025 Mar 10;12(3):345. doi: 10.3390/children12030345. Children (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vicentini C., Vola L., Previti C., Brescia V., Dal Mas F., Zotti C.M., Bert F. Antimicrobial Stewardship Strategies Including Point-of-Care Testing (POCT) for Pediatric Patients with Upper-Respiratory-Tract Infections in Primary Care: A Systematic Review of Economic Evaluations. Antibiotics. 2022;11:1139. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11081139. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

