Utilizing COVID-19 as a Model for Diagnostics Using an Electrochemical Sensor
- PMID: 38931556
- PMCID: PMC11207896
- DOI: 10.3390/s24123772
Utilizing COVID-19 as a Model for Diagnostics Using an Electrochemical Sensor
Abstract
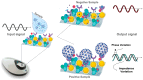
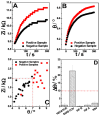
This paper reports a rapid and sensitive sensor for the detection and quantification of the COVID-19 N-protein (N-PROT) via an electrochemical mechanism. Single-frequency electrochemical impedance spectroscopy was used as a transduction method for real-time measurement of the N-PROT in an immunosensor system based on gold-conjugate-modified carbon screen-printed electrodes (Cov-Ag-SPE). The system presents high selectivity attained through an optimal stimulation signal composed of a 0.0 V DC potential and 10 mV RMS-1 AC signal at 100 Hz over 300 s. The Cov-Ag-SPE showed a log response toward N-PROT detection at concentrations from 1.0 ng mL-1 to 10.0 μg mL-1, with a 0.977 correlation coefficient for the phase (θ) variation. An ML-based approach could be created using some aspects observed from the positive and negative samples; hence, it was possible to classify 252 samples, reaching 83.0, 96.2 and 91.3% sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy, respectively, with confidence intervals (CI) ranging from 73.0 to 100.0%. Because impedance spectroscopy measurements can be performed with low-cost portable instruments, the immunosensor proposed here can be applied in point-of-care diagnostics for mass testing, even in places with limited resources, as an alternative to the common diagnostics methods.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; electrochemical sensor; nucleocapsid protein; point-of-care test; screen-printed electrodes.
Conflict of interest statement
Marcus V.M. Figueredo is the CEO of Hilab; Sérgio Rogal-Junior is the CTO of Hilab; Diego R.P. Nicollete is R&D manager at Hilab; Ava Gevaerd is electrochemical manager at Hilab; Emmanuelle A. Carneiro and Jeferson L. Gogola are health researchers at Hilab; Luis F. Hartmann is head of R&D at Hilab; João V. Predebon and Adriano Timm are R&D researchers at Hilab; Carlos Rochitti is a researcher at PUC University; Gustavo L. Marques and Maira M.O.N. Loesch are assistant doctors at Marcelino Champagnat Hospital; Bernardo M.M. de Almeida is medical director at Hilab. Other remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Voltammetric-based immunosensor for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antigen.Mikrochim Acta. 2021 May 26;188(6):199. doi: 10.1007/s00604-021-04867-1. Mikrochim Acta. 2021. PMID: 34041585 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Low-Cost Cotton-Tipped Electrochemical Immunosensor for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2.Anal Chem. 2021 Jan 26;93(3):1826-1833. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c04719. Epub 2020 Dec 28. Anal Chem. 2021. PMID: 33370087
-
Sensitive sandwich-type electrochemical SARS-CoV‑2 nucleocapsid protein immunosensor.Mikrochim Acta. 2021 Nov 23;188(12):425. doi: 10.1007/s00604-021-05092-6. Mikrochim Acta. 2021. PMID: 34812927 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 using potential point-of-care electrochemical immunosensor: Toward the future prospects.Int Rev Immunol. 2021;40(1-2):126-142. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2021.1872566. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Int Rev Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33448909 Review.
-
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy in the Characterisation and Application of Modified Electrodes for Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors.Molecules. 2022 Feb 23;27(5):1497. doi: 10.3390/molecules27051497. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35268599 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Qazi S., Raza K. Smart Biosensors in Medical Care. Elsevier Inc.; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2020. Smart Biosensors for an Efficient Point of Care (PoC) Health Management; pp. 65–85.
-
- Tertis M., Hosu O., Florea A., Cristea C. Immunodiagnostic Technologies from Laboratory to Point-of-Care Testing. Springer; Singapore: 2021. Biosensors for Clinical Samples: Consideration and Approaches; pp. 1–32.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

