Development of Clarstatin, a Novel Drug Lead for the Therapy of Autoimmune Uveitis
- PMID: 38931845
- PMCID: PMC11206685
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16060723
Development of Clarstatin, a Novel Drug Lead for the Therapy of Autoimmune Uveitis
Abstract
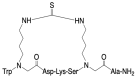
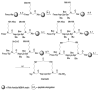
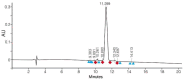
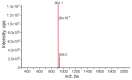
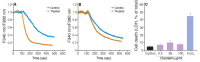
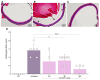
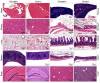
We describe the design, synthesis, and activity of a potent thiourea-bridged backbone cyclic peptidomimetic known as Clarstatin, comprising a 5-amino acid sequence (Q/D)1-(R/K)2-X3-X4-A5-(Gln/Asp)1-(Arg/Lys)2-AA3-AA4-Ala5-based on a motif called "shared epitope (SE)", specifically present in specific alleles of the HLA-DRB1 gene. This SE binds to a particular site within the proline reach domain (P-domain) of the cell surface-calreticulin (CS-CRT). CS-CRT is a multifunctional endoplasmic reticulum (ER) calcium-binding protein that is located on the cell surface of T cells and triggers innate immune signaling, leading to the development of inflammatory autoimmune diseases. The development of Clarstatin was based on the parent peptide W-G-D1-K2-S3-G4-A5- derived from the active region of the SE. Following the design based on the cycloscan method, the synthesis of Clarstatin was performed by the Fmoc solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) method, purified by HPLC to 96% homogeneity, and its structure was confirmed by LC-MS. Clarstatin reduced calcium levels in Jurkat lymphocyte cultures, ameliorated uveitis in vivo in the experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU) mice model, and was safe upon acute toxicity evaluation. These findings identify Clarstatin as a promising lead compound for future drug development as a novel class of therapeutic agents in the therapy of uveitis.
Keywords: backbone cyclization; calreticulin; experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis; inflammatory autoimmune diseases; peptidomimetic; peptomer; thiourea-bridged; uveitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Clarstatin, a Shared-Epitope-Antagonistic Cyclic Peptide, on Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis in Mice.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025 Jan 2;66(1):13. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.1.13. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 39775697 Free PMC article.
-
[The onset mechanism of experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis induced by interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 1992 Dec;96(12):1580-607. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 1992. PMID: 1283051 Japanese.
-
Amelioration of experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis (EAU) with an inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB), pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate.J Leukoc Biol. 2006 Jun;79(6):1193-201. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0805453. Epub 2006 Mar 30. J Leukoc Biol. 2006. PMID: 16574770
-
[Therapeutic effect of the low molecular weight inhibitor of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway on experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2010 Nov;114(11):944-54. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2010. PMID: 21141074 Review. Japanese.
-
[Intraocular inflammation and homeostasis of the eye].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2009 Mar;113(3):344-77; discussion 378. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2009. PMID: 19348183 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Clarstatin, a Shared-Epitope-Antagonistic Cyclic Peptide, on Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis in Mice.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025 Jan 2;66(1):13. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.1.13. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 39775697 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rosenbaum J.T., Bodaghi B., Couto C., Zierhut M., Acharya N., Pavesio C., Tay-Kearney M.L., Neri P., Douglas K., Pathai S., et al. New Observations and Emerging Ideas in Diagnosis and Management of Non-Infectious Uveitis: A Review. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019;49:438–445. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2019.06.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mangalam A.K., Rajagopalan G., Taneja V., David C.S. HLA Class II Transgenic Mice Mimic Human Inflammatory Diseases. Adv. Immunol. 2008;97:65–147. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

