Predicting ADMET Properties from Molecule SMILE: A Bottom-Up Approach Using Attention-Based Graph Neural Networks
- PMID: 38931898
- PMCID: PMC11207804
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16060776
Predicting ADMET Properties from Molecule SMILE: A Bottom-Up Approach Using Attention-Based Graph Neural Networks
Abstract
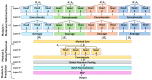
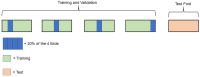
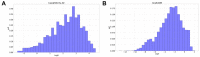
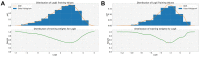
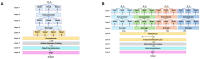
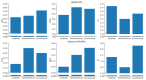
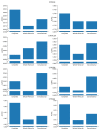
Understanding the pharmacokinetics, safety and efficacy of candidate drugs is crucial for their success. One key aspect is the characterization of absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity (ADMET) properties, which require early assessment in the drug discovery and development process. This study aims to present an innovative approach for predicting ADMET properties using attention-based graph neural networks (GNNs). The model utilizes a graph-based representation of molecules directly derived from Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System (SMILE) notation. Information is processed sequentially, from substructures to the whole molecule, employing a bottom-up approach. The developed GNN is tested and compared with existing approaches using six benchmark datasets and by encompassing regression (lipophilicity and aqueous solubility) and classification (CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 inhibition) tasks. Results show the effectiveness of our model, which bypasses the computationally expensive retrieval and selection of molecular descriptors. This approach provides a valuable tool for high-throughput screening, facilitating early assessment of ADMET properties and enhancing the likelihood of drug success in the development pipeline.
Keywords: ADMET prediction; attention-based architecture; graph neural network; model-based drug development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Improved GNNs for Log D7.4 Prediction by Transferring Knowledge from Low-Fidelity Data.J Chem Inf Model. 2023 Apr 24;63(8):2345-2359. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.2c01564. Epub 2023 Mar 31. J Chem Inf Model. 2023. PMID: 37000044
-
Optimal Transport Based Graph Kernels for Drug Property Prediction.IEEE Open J Eng Med Biol. 2024 Oct 14;6:152-157. doi: 10.1109/OJEMB.2024.3480708. eCollection 2025. IEEE Open J Eng Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39906265 Free PMC article.
-
Conformalized Graph Learning for Molecular ADMET Property Prediction and Reliable Uncertainty Quantification.J Chem Inf Model. 2024 Dec 9;64(23):8705-8717. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.4c01139. Epub 2024 Nov 21. J Chem Inf Model. 2024. PMID: 39571080
-
A review on machine learning approaches and trends in drug discovery.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Aug 12;19:4538-4558. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.08.011. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34471498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improving ADMET Prediction Accuracy for Candidate Drugs: Factors to Consider in QSPR Modeling Approaches.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(3):222-242. doi: 10.2174/0115680266280005231207105900. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38083894 Review.
Cited by
-
Leveraging machine learning models in evaluating ADMET properties for drug discovery and development.ADMET DMPK. 2025 Jun 7;13(3):2772. doi: 10.5599/admet.2772. eCollection 2025. ADMET DMPK. 2025. PMID: 40585410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial: Revolutionizing life sciences: the nobel leap in artificial intelligence-driven biomodeling.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Jan 3;11:1540823. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1540823. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 39830980 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Discovery of Small Molecules Targeting Norovirus 3CL Protease by Multi-Stage Virtual Screening.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 12;26(12):5625. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125625. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565089 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

