C-Terminal Binding Protein: Regulator between Viral Infection and Tumorigenesis
- PMID: 38932279
- PMCID: PMC11209466
- DOI: 10.3390/v16060988
C-Terminal Binding Protein: Regulator between Viral Infection and Tumorigenesis
Abstract
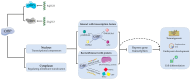
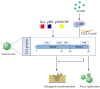
C-terminal binding protein (CtBP), a transcriptional co-repressor, significantly influences cellular signaling, impacting various biological processes including cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and immune responses. The CtBP family comprises two highly conserved proteins, CtBP1 and CtBP2, which have been shown to play critical roles in both tumorigenesis and the regulation of viral infections. Elevated CtBP expression is noted in various tumor tissues, promoting tumorigenesis, invasiveness, and metastasis through multiple pathways. Additionally, CtBP's role in viral infections varies, exhibiting differing or even opposing effects depending on the virus. This review synthesizes the advances in CtBP's function research in viral infections and virus-associated tumorigenesis, offering new insights into potential antiviral and anticancer strategies.
Keywords: C-terminal binding protein (CtBP); corepressor; transcriptional coregulator; tumorigenesis; viral infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transforming activity and therapeutic targeting of C-terminal-binding protein 2 in Apc-mutated neoplasia.Oncogene. 2017 Aug 17;36(33):4810-4816. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.106. Epub 2017 Apr 17. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28414304 Free PMC article.
-
Active-Site Tryptophan, the Target of Antineoplastic C-Terminal Binding Protein Inhibitors, Mediates Inhibitor Disruption of CtBP Oligomerization and Transcription Coregulatory Activities.Mol Pharmacol. 2019 Jul;96(1):99-108. doi: 10.1124/mol.118.114363. Epub 2019 Apr 29. Mol Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31036695 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of CtBP family protein isoforms in breast cancer and their role in chemoresistance.Biol Cell. 2010 Jan;103(1):1-19. doi: 10.1042/BC20100067. Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20964627 Free PMC article.
-
CtBP- an emerging oncogene and novel small molecule drug target: Advances in the understanding of its oncogenic action and identification of therapeutic inhibitors.Cancer Biol Ther. 2017 Jun 3;18(6):379-391. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2017.1323586. Epub 2017 May 22. Cancer Biol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28532298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation by C-terminal binding proteins.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39(9):1593-607. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2007.01.025. Epub 2007 Feb 4. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17336131 Review.
References
-
- Boyd J.M., Subramanian T., Schaeper U., La Regina M., Bayley S., Chinnadurai G. A region in the C-terminus of adenovirus 2/5 E1a protein is required for association with a cellular phosphoprotein and important for the negative modulation of T24-ras mediated transformation, tumorigenesis and metastasis. EMBO J. 1993;12:469–478. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05679.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Banerjee A., Birts C.N., Darley M., Parker R., Mirnezami A.H., West J., Cutress R.I., Beers S.A., Rose-Zerilli M.J.J., Blaydes J.P. Stem cell-like breast cancer cells with acquired resistance to metformin are sensitive to inhibitors of NADH-dependent CtBP dimerization. Carcinogenesis. 2019;40:871–882. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgy174. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

