Nano-Pulse Treatment Overcomes the Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment to Elicit In Situ Vaccination Protection against Breast Cancer
- PMID: 38932362
- PMCID: PMC11209453
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines12060633
Nano-Pulse Treatment Overcomes the Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment to Elicit In Situ Vaccination Protection against Breast Cancer
Abstract
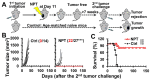
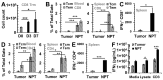
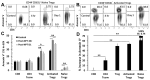
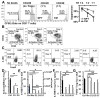
We previously reported that nano-pulse treatment (NPT), a pulsed power technology, resulted in 4T1-luc mammary tumor elimination and a strong in situ vaccination, thereby completely protecting tumor-free animals against a second live tumor challenge. The mechanism whereby NPT mounts effective antitumor immune responses in the 4T1 breast cancer predominantly immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) remains unanswered. In this study, orthotopic 4T1 mouse breast tumors were treated with NPT (100 ns, 50 kV/cm, 1000 pulses, 3 Hz). Blood, spleen, draining lymph nodes, and tumors were harvested at 4-h, 8-h, 1-day, 3-day, 7-day, and 3-month post-treatment intervals for the analysis of frequencies, death, and functional markers of various immune cells in addition to the suppressor function of regulatory T cells (Tregs). NPT was verified to elicit strong in situ vaccination (ISV) against breast cancer and promote both acute and long-term T cell memory. NPT abolished immunosuppressive dominance systemically and in the TME by substantially reducing Tregs, myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). NPT induced apoptosis in Tregs and TAMs. It also functionally diminished the Treg suppression capacity, explained by the downregulation of activation markers, particularly 4-1BB and TGFβ, and a phenotypic shift from predominantly activated (CD44+CD62L-) to naïve (CD44-CD62L+) Tregs. Importantly, NPT selectively induced apoptosis in activated Tregs and spared effector CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. These changes were followed by a concomitant rise in CD8+CD103+ tissue-resident memory T cells and TAM M1 polarization. These findings indicate that NPT effectively switches the TME and secondary lymphatic systems from an immunosuppressive to an immunostimulatory state, allowing cytotoxic T cell function and immune memory formation to eliminate cancer cells and account for the NPT in situ vaccination.
Keywords: apoptosis; breast cancer; immunosuppression; in situ vaccination; memory T cells; myeloid-derived suppressor cells; nano-pulse treatment (NPT); regulatory T cells; tumor microenvironment; tumor-associated macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
S.J. Beebe owns stock in Pulse Biosciences, Inc. (Hayward, CA, USA). The other authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Aiduqing formula inhibits breast cancer metastasis by suppressing TAM/CXCL1-induced Treg differentiation and infiltration.Cell Commun Signal. 2021 Aug 30;19(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s12964-021-00775-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 34461944 Free PMC article.
-
Delicaflavone reactivates anti-tumor immune responses by abrogating monocytic myeloid cell-mediated immunosuppression.Phytomedicine. 2023 Jan;108:154508. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154508. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 36332384
-
Therapeutic targeting with DABIL-4 depletes myeloid suppressor cells in 4T1 triple-negative breast cancer model.Mol Oncol. 2021 May;15(5):1330-1344. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12938. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Mol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33682324 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of the tumor immune microenvironment by metformin.J Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Sep;16(3):333-348. doi: 10.1007/s12079-021-00648-w. Epub 2021 Oct 5. J Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 34611852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor Microenvironment as A "Game Changer" in Cancer Radiotherapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 29;20(13):3212. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133212. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31261963 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

