The generalized odd log-logistic-G regression with interval-censored survival data
- PMID: 38933143
- PMCID: PMC11198143
- DOI: 10.1080/02664763.2023.2230533
The generalized odd log-logistic-G regression with interval-censored survival data
Abstract
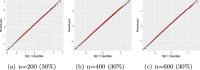
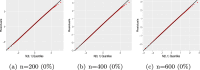
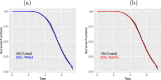
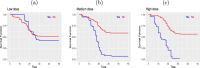
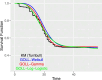
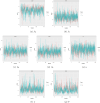
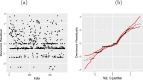
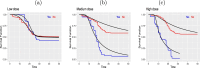
The article proposes a new regression based on the generalized odd log-logistic family for interval-censored data. The survival times are not observed for this type of data, and the event of interest occurs at some random interval. This family can be used in interval modeling since it generalizes some popular lifetime distributions in addition to its ability to present various forms of the risk function. The estimation of the parameters is addressed by the classical and Bayesian methods. We examine the behavior of the estimates for some sample sizes and censorship percentages. Selection criteria, likelihood ratio tests, residual analysis, and graphical techniques assess the goodness of fit of the fitted models. The usefulness of the proposed models is red shown by means of two real data sets.
Keywords: 62N01; Bayesian inference; generalized odd log-logistic family; interval-censored data; regression model; residual analysis.
© 2023 Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Alizadeh M., Korkmaz M.Ç., Almamy J.A., and Ahmed A.A.E., Another odd log-logistic logarithmic class of continuous distributions, Istatistikçiler Dergisi: Istatistik & Aktuerya 11 (2018), pp. 55–72.
-
- Atkinson A.C., Two graphical displays for outlying and influential observations in regression, Biometrika 68 (1981), pp. 13–20.
-
- Basak P., Linero A.R., Sinha D., and Lipsitz S., Semiparametric analysis of clustered interval-censored survival data using soft Bayesian additive regression trees (sbart), Biometrics 78 (2021), pp. 1–14. - PubMed
-
- Betensky R.A. and Finkelstein D.M., Testing for dependence between failure time and visit compliance with interval-censored data, Biometrics 58 (2002), pp. 58–63. - PubMed
-
- Bogaerts K. and Lesaffre E., Estimating local and global measures of association for bivariate interval censored data with a smooth estimate of the density, Stat. Med. 27 (2008), pp. 5941–5955. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
