Necroptosis in bacterial infections
- PMID: 38933265
- PMCID: PMC11199740
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1394857
Necroptosis in bacterial infections
Abstract
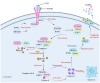
Necroptosis, a recently discovered form of cell-programmed death that is distinct from apoptosis, has been confirmed to play a significant role in the pathogenesis of bacterial infections in various animal models. Necroptosis is advantageous to the host, but in some cases, it can be detrimental. To understand the impact of necroptosis on the pathogenesis of bacterial infections, we described the roles and molecular mechanisms of necroptosis caused by different bacterial infections in this review.
Keywords: bacterial infection; inflammatory cells; mlkl; necroptosis; ripk1; ripk3.
Copyright © 2024 Yu, Yuan, Shi, Dai, Yue and Yan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Opposite Effects of Apoptotic and Necroptotic Cellular Pathways on Rotavirus Replication.J Virol. 2022 Jan 12;96(1):e0122221. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01222-21. Epub 2021 Oct 20. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34668777 Free PMC article.
-
RIPK3-Dependent Recruitment of Low-Inflammatory Myeloid Cells Does Not Protect from Systemic Salmonella Infection.mBio. 2020 Oct 6;11(5):e02588-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02588-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 33024046 Free PMC article.
-
PANoptosis in Bacterial Infections: A Double-Edged Sword Balancing Host Immunity and Pathogenesis.Pathogens. 2025 Jan 8;14(1):43. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14010043. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 39861004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surviving death: emerging concepts of RIPK3 and MLKL ubiquitination in the regulation of necroptosis.FEBS J. 2023 Jan;290(1):37-54. doi: 10.1111/febs.16255. Epub 2021 Nov 16. FEBS J. 2023. PMID: 34710282 Review.
-
Dectin-1-induced RIPK1 and RIPK3 activation protects host against Candida albicans infection.Cell Death Differ. 2019 Dec;26(12):2622-2636. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0323-8. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Cell Death Differ. 2019. PMID: 30944411 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Different Forms of Regulated Cell Death in Type-2-Diabetes-Mellitus-Related Osteoporosis: A Focus on Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 6;26(9):4417. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094417. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stress granules and cell death: crosstalk and potential therapeutic strategies in infectious diseases.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Jul 5;16(1):495. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07800-z. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40617807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neisseria meningitidis activates pyroptotic pathways in a mouse model of meningitis: role of a two-partner secretion system.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Sep 23;14:1384072. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1384072. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39376663 Free PMC article.
-
Orientia tsutsugamushi Modulates RIPK3 Cellular Levels but Does Not Inhibit Necroptosis.Pathogens. 2025 May 14;14(5):478. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14050478. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40430799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Awad MM, Bryant AE, Stevens DL, Rood JI. Virulence studies on chromosomal alpha-toxin and theta-toxin mutants constructed by allelic exchange provide genetic evidence for the essential role of alpha-toxin in Clostridium perfringens-mediated gas gangrene. Mol Microbiol. (1995) 15:191–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02234.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhu W, Zhang F, Lu J, Ma C, Shen L, Hu D, et al. . The analysis of Modified Qing' E Formula on the differential expression of exosomal miRNAs in the femoral head bone tissue of mice with steroid-induced ischemic necrosis of femoral head. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:954778. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.954778 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

