Exploration of chemical components and metabolite synthesis pathways in eight Ephedra species based on HS-GC-MS and UPLC-Q-TOF-MS
- PMID: 38933459
- PMCID: PMC11205265
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1421008
Exploration of chemical components and metabolite synthesis pathways in eight Ephedra species based on HS-GC-MS and UPLC-Q-TOF-MS
Abstract
Objective: Ephedra, widely used in clinical practice as a medicinal herb, belongs to the genus Ephedra in the family Ephedraceae. However, the presence of numerous Ephedra varieties and variants requires differentiation for accurate identification.
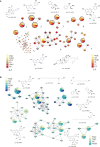
Methods: In this study, we employed headspace gas chromatography mass spectrometry (HS-GC-MS), ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS), and global natural products social molecular networking (GNPS) for chemical component identification. Chemometric analysis was used to analyze the differential components. Metabolic analysis and Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) enrichment were utilized to explore the synthesis pathways of different components.
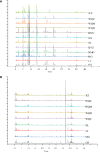
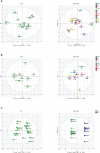
Result: A total of 83 volatile and 79 non-volatile components were identified in Ephedra species. Differential analysis revealed that among the eight Ephedra stems, 18 volatile and 19 non-volatile differential compounds were discovered, whereas Ephedra roots exhibited 21 volatile and 17 non-volatile markers. Volatile compounds were enriched in four synthetic pathways, while non-volatile components were enriched in five pathways among the differentiated components.
Conclusion: This study is the first to conduct a comparative analysis of chemical components in different Ephedra species and parts. It provides a foundational reference for authenticating Ephedra herbs, evaluating medicinal resources, and comparing quality in future studies.
Keywords: Ephedra species; HS-GC-MS; UPLC-Q-ToF-MS; chemical component; molecular network; synthetic route.
Copyright © 2024 Guo, Yang, Li, An, Liu, Cheng, Hou, Guo and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Al-Rimawi F., Abu-Lafi S., Abbadi J., Alamarneh A. A., Sawahreh R. A., Odeh I. (2017). Analysis of phenolic and flavonoids of wild Ephedra alata plant extracts by LC/PDA and LC/MS and their antioxidant activity. Afr. J. Traditional Complementary Altern. Medicines 14, 130–141. doi: 10.21010/ajtcam.v14i2.14 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Commission C. P. (2020). Pharmacopoeia of the people's Republic of China (Beijing: China Medical Science Press; ).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

