Novel Combination Treatment for Melanoma: FLASH Radiotherapy and Immunotherapy Delivered by a Radiopaque and Radiation Responsive Hydrogel
- PMID: 38933522
- PMCID: PMC11198981
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.3c01390
Novel Combination Treatment for Melanoma: FLASH Radiotherapy and Immunotherapy Delivered by a Radiopaque and Radiation Responsive Hydrogel
Abstract
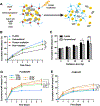
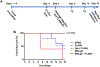
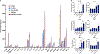
Immunotherapies have become the standard treatment for melanoma. To further improve patient responses, combinations of immunotherapies and radiotherapy (RT) are being studied, since radiotherapies can potentially provide additional immune stimulation, in addition to direct antitumor effects. FLASH-RT is a novel, ultrahigh dose rate, radiation delivery approach, with the potential of at least equivalent tumor control efficacy and reduced damage to healthy tissue. However, the effects of combining FLASH-RT and immunotherapy have not been extensively studied in melanoma. Toll-like receptor (TLR) agonists, such as imiquimod (IMQ), are potent immunostimulatory agents, although their utility is limited due to poor solubility and systemic side effects. We therefore developed a novel combination therapy for melanoma consisting of IMQ delivered to the tumor via a radiopaque and radiation responsive hydrogel combined with FLASH-RT. We found that FLASH was able to effectively stimulate IMQ release from the hydrogel. In addition, we found that the combination of FLASH and released IMQ resulted in synergistic melanoma cell killing in vitro. The combination therapy reduced tumor growth compared to controls, enhanced survival, and resulted in remarkable enhancements in certain tumor cytokine levels. CT imaging allowed the hydrogel to be monitored in vivo. In addition, no adverse effects of the treatment were observed. Overall, this IMQ-gel and FLASH-RT combination may have potential as an improved treatment for melanoma and indicates that the interactions of FLASH-RT and TLR agonists merit further study.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

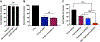

References
-
- Shain AH; Bastian BC From melanocytes to melanomas. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16 (6), 345–358. - PubMed
-
- Lancellotta V; Del Regno L; Di Stefani A; Fionda B; Marazzi F; Rossi E; Balducci M; Pampena R; Morganti AG; Mangoni M; et al. The role of stereotactic radiotherapy in addition to immunotherapy in the management of melanoma brain metastases: results of a systematic review. Radiol. Med 2022, 127 (7), 773–783. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bourhis J; Sozzi WJ; Jorge PG; Gaide O; Bailat C; Duclos F; Patin D; Ozsahin M; Bochud F; Germond JF; et al. Treatment of a first patient with FLASH-radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol 2019, 139, 18–22. - PubMed
-
- Kang HY; Park TJ; Jin SH Imiquimod, a Toll-like receptor 7 agonist, inhibits melanogenesis and proliferation of human melanocytes. J. Invest. Dermatol 2009, 129 (1), 243–246. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
