Investigating mechanistic insights of curcumin in blocking the Interleukin-8 signaling pathway associated with Breast Cancer: An in-silico approach
- PMID: 38934013
- PMCID: PMC11201349
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2024.104035
Investigating mechanistic insights of curcumin in blocking the Interleukin-8 signaling pathway associated with Breast Cancer: An in-silico approach
Abstract
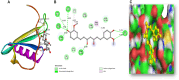
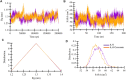
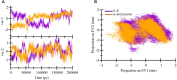
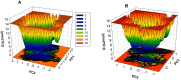
Interleukin-8 (IL-8) is a chemokine, a type of signaling molecule that has a role in immunological responses and inflammation. In recent years, IL-8 is additionally related to cancer growth and recurrence. Breast cancer growth, progression, and metastatic development are all linked to IL-8. Breast cancer cells are known to develop faster when IL-8 stimulates their proliferation and survival. It can also cause angiogenesis, or the creation of new blood vessels, which is necessary for tumor nutrition and growth. IL-8 and curcumin have been subjects of interest in drug design, particularly in the context of inflammation-related disorders and cancer. This study aims to give an overview of the role of IL-8. Inhibitor-based treatment approaches were being used to target IL-8 with curcumin. Molecular docking method was employed to find a potential interaction to supress competitive inhibition of IL-8 with curcumin. PASS analysis and ADMET characteristics were also being carried out. In the end, IL-8 complexed with curcumin is chosen for MD simulations. Overall, our results showed that during the simulation, the complex stayed comparatively stable. It is also possible to investigate curcumin further as a possible treatment option. The combined results imply that IL-8 and their genetic alterations can be studied in precision cancer therapeutic treatments, utilizing target-driven therapy and early diagnosis.
Keywords: ADMET; FEL; IL-8 (Interleukin-8); MD simulations; Molecular Docking.
© 2024 The Authors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Curcumin and Plumbagin Synergistically Target the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway: A Prospective Role in Cancer Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 2;24(7):6651. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076651. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047624 Free PMC article.
-
BDMC-A, an analog of curcumin, inhibits markers of invasion, angiogenesis, and metastasis in breast cancer cells via NF-κB pathway--A comparative study with curcumin.Biomed Pharmacother. 2015 Aug;74:178-86. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2015.07.024. Epub 2015 Aug 15. Biomed Pharmacother. 2015. PMID: 26349982
-
Curcumin blocks interleukin-1 signaling in chondrosarcoma cells.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 5;9(6):e99296. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099296. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24901233 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin: An Effective Inhibitor of Interleukin-6.Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(6):921-931. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666161006151605. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 27719643 Review.
-
Curcumin as an Alternative Epigenetic Modulator: Mechanism of Action and Potential Effects.Front Genet. 2019 Jun 4;10:514. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00514. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31214247 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beg, A., Parveen, R., 2021. Role of bioinformatics in cancer research and drug development, in: Translational Bioinformatics in Healthcare and Medicine. Elsevier, pp. 141–148.
-
- Beg A., Khan F.I., Lobb K.A., Islam A., Ahmad F., Hassan M.I. High throughput screening, docking, and molecular dynamics studies to identify potential inhibitors of human calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2019;37:2179–2192. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

