Core regions in immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancers essential for survival of non-Hodgkin lymphoma cells are identified by a CRISPR interference screen
- PMID: 38934080
- PMCID: PMC11609794
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2023.284672
Core regions in immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancers essential for survival of non-Hodgkin lymphoma cells are identified by a CRISPR interference screen
Abstract
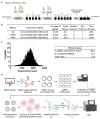
Chromosomal translocations in non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) result in activation of oncogenes by placing them under the regulation of immunoglobulin heavy chain (IGH) super-enhancers. Aberrant expression of translocated oncogenes induced by enhancer activity can contribute to lymphomagenesis. The role of the IGH enhancers in normal B-cell development is well established, but knowledge regarding the precise mechanisms of their involvement in control of the translocated oncogenes is limited. The goal of this project was to define the critical regions in the IGH regulatory elements and identify enhancer RNA (eRNA). We designed a single guide RNA library densely covering the IGH enhancers and performed tiling CRISPR interference screens in three NHL cell lines. This revealed three regions crucial for NHL cell growth. With chromatin- enriched RNA sequencing we showed transcription from the core enhancer regions and subsequently validated expression of the eRNA in a panel of NHL cell lines and tissue samples. Inhibition of the essential IGH enhancer regions decreased expression of eRNA and translocated oncogenes in several NHL cell lines. The observed expression and growth patterns were consistent with the breakpoints in the IGH locus. Moreover, targeting the Eμ enhancer resulted in loss of B-cell receptor expression. In a Burkitt lymphoma cell line, MYC overexpression partially rescued the phenotype induced by IGH enhancer inhibition. Our results indicated the most critical regions in the IGH enhancers and provided new insights into the current understanding of the role of IGH enhancers in B-cell NHL. As such, this study forms a basis for development of potential therapeutic approaches.
Figures




References
-
- Sedeta E, Ilerhunmwuwa N, Wasifuddin M, et al. Epidemiology of non-Hodgkin lymphoma: global patterns of incidence, mortality, and trends. Blood. 2022;140(Supplement 1):5234-5235.
-
- Küppers R, Dalla-Favera R. Mechanisms of chromosomal translocations in B cell lymphomas. Oncogene. 2001;20(40):5580-5594. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

