Determining Asymmetry Thresholds in Anophthalmia/Microphthalmia Using a Three-dimensional Animated Model
- PMID: 38934734
- PMCID: PMC11692783
- DOI: 10.1097/IOP.0000000000002711
Determining Asymmetry Thresholds in Anophthalmia/Microphthalmia Using a Three-dimensional Animated Model
Abstract
Purpose: Congenital microphthalmia and anophthalmia are rare development disorders with underdevelopment of the orbital region, resulting in asymmetry of the face. No clear guidelines exist to determine when these deviations are acceptable.
Methods: The face of a healthy 6-year-old child was three-dimensionally scanned. On this scan, we modeled various incremental degrees of facial asymmetries using three-dimensional modeling software. We modeled for smaller palpebral fissures, sunken eyes, and downward displacement of the eye. We also tested whether adjusting the vertical palpebral fissure height in relation to the horizontal palpebral fissure width affected perception. A total of 22 videos were created in which the model turned the head horizontally and vertically. We created a questionnaire asking raters how acceptable the face is, on a linear scale from 0 to 10.
Results: Results showed a correlation between the degree of asymmetry and the acceptability score of the raters. Enophthalmos of ≥6 mm, palpebral fissure width ≤79% compared with the other eye, and 2 mm or more downward displacement of the eye resulted in a significant different acceptability score. The desire for correction was strongly increased when these thresholds were exceeded. Adjusting the vertical palpebral fissure height to the horizontal palpebral fissure width resulted in a worse acceptability score.
Conclusion: A unilateral sunken eye (enophthalmos) of 6 mm or more, asymmetric horizontal palpebral fissure length of ≤79%, and a lower position of one eye of more than 2 mm resulted in unacceptable judgment. These data can be used to evaluate treatment outcome in children treated for congenital microphthalmia and anophthalmia.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Society of Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
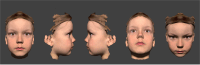


References
-
- Barbeau EJ, Taylor MJ, Regis J, et al. . Spatio temporal dynamics of face recognition. Cereb Cortex. 2008;18:997–1009. - PubMed
-
- Sekuler AB, Gaspar CM, Gold JM, et al. . Inversion leads to quantitative, not qualitative, changes in face processing. Curr Biol. 2004;14:391–396. - PubMed
-
- Godoy A, Ishii M, Byrne PJ, et al. . The straight truth: measuring observer attention to the crooked nose. Laryngoscope. 2011;121:937–941. - PubMed
-
- Ishii L, Carey J, Byrne P, et al. . Measuring attentional bias to peripheral facial deformities. Laryngoscope. 2009;119:459–465. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

