Adjuvant Trastuzumab Emtansine Versus Paclitaxel Plus Trastuzumab for Stage I Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Positive Breast Cancer: 5-Year Results and Correlative Analyses From ATEMPT
- PMID: 38935923
- PMCID: PMC11527383
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.23.02170
Adjuvant Trastuzumab Emtansine Versus Paclitaxel Plus Trastuzumab for Stage I Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Positive Breast Cancer: 5-Year Results and Correlative Analyses From ATEMPT
Abstract
Purpose: Long-term outcomes of patients with stage I human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive breast cancer receiving adjuvant trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) remain undefined, and prognostic predictors represent an unmet need.
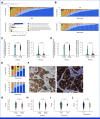
Methods: In the ATEMPT phase II trial, patients with stage I centrally confirmed HER2-positive breast cancer were randomly assigned 3:1 to adjuvant T-DM1 for 1 year or paclitaxel plus trastuzumab (TH). Coprimary objectives were to compare the incidence of clinically relevant toxicities between arms and to evaluate invasive disease-free survival (iDFS) with T-DM1. Correlative analyses included the HER2DX genomic tool, multiomic evaluations of HER2 heterogeneity, and predictors of thrombocytopenia.
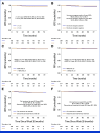
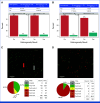
Results: After a median follow-up of 5.8 years, 11 iDFS events were observed in the T-DM1 arm, consistent with a 5-year iDFS of 97.0% (95% CI, 95.2 to 98.7). At 5 years, the recurrence-free interval (RFI) was 98.3% (95% CI, 97.0 to 99.7), the overall survival was 97.8% (95% CI, 96.3 to 99.3), and the breast cancer-specific survival was 99.4% (95% CI, 98.6 to 100). Comparable iDFS was observed with T-DM1 irrespective of tumor size, hormone receptor status, centrally determined HER2 immunohistochemical score, and receipt of T-DM1 for more or less than 6 months. Although ATEMPT was not powered for this end point, the 5-year iDFS in the TH arm was 91.1%. Among patients with sufficient tissue for HER2DX testing (n = 187), 5-year outcomes significantly differed according to HER2DX risk score, with better RFI (98.1% v 81.8%, hazard ratio [HR], 0.10, P = .01) and iDFS (96.3% v 81.8%, HR, 0.20, P = .047) among patients with HER2DX low-risk versus high-risk tumors, respectively.
Conclusion: Adjuvant T-DM1 for 1 year leads to outstanding long-term outcomes for patients with stage I HER2-positive breast cancer. A high HER2DX risk score predicted a higher risk of recurrence in ATEMPT.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01853748.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures



Comment in
-
T-DM1: a promising adjuvant therapy option for stage I HER2-positive breast cancer-interpreting ATEMPT trial results from a clinical perspective.Gland Surg. 2025 Apr 30;14(4):785-790. doi: 10.21037/gs-2025-23. Epub 2025 Apr 25. Gland Surg. 2025. PMID: 40405946 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
New emerging data on adjuvant systemic therapy for stage I HER2 positive breast cancer.Gland Surg. 2025 May 30;14(5):803-806. doi: 10.21037/gs-2025-41. Epub 2025 May 27. Gland Surg. 2025. PMID: 40546847 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Curigliano G, Viale G, Bagnardi V, et al. Clinical relevance of HER2 overexpression/amplification in patients with small tumor size and node-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:5693–5699. - PubMed
-
- Tolaney SM, Tarantino P, Graham N, et al. Adjuvant paclitaxel and trastuzumab for node-negative, HER2-positive breast cancer: Final 10-year analysis of the open-label, single-arm, phase 2 APT trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023;24:273–285. - PubMed
-
- Cardoso F, Kyriakides S, Ohno S, et al. Early breast cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2019;30:1194–1220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

