Efficacy and Safety of BP02 (Trastuzumab Biosimilar) in HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Multicenter Phase III Study
- PMID: 38937403
- PMCID: PMC11263219
- DOI: 10.1007/s40261-024-01374-y
Efficacy and Safety of BP02 (Trastuzumab Biosimilar) in HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Multicenter Phase III Study
Abstract
Background and objective: Trastuzumab targets human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) receptors and is indicated for treating HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. BP02, a recombinant IgG1 kappa humanized monoclonal antibody, is being developed as a trastuzumab biosimilar. The objective of this study was to evaluate the equivalence of BP02 with reference trastuzumab (RT: Herceptin®-EU) in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer.
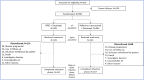
Methods: This double-blinded, 1:1 randomized, parallel-group, active-controlled, phase III equivalence trial recruited women aged 18-75 years with histologically/cytologically confirmed HER2- positive, locally recurrent or metastatic breast cancer with systemic metastasis, from 59 sites in India. Patients were randomly allocated 1:1 stratified by estrogen receptor/progesterone receptor status to receive BP02/RT (8-mg/kg loading dose on day 1-cycle 1, 6 mg/kg on day 1-cycles 2-8, of each 3-week cycle) combined with docetaxel (75 mg/m2 on day 1-cycles 1-8) [induction phase]. Participants with complete or partial response, or stable disease at the end of the induction phase continued the study drug until disease progression/treatment discontinuation [maintenance phase]. The primary efficacy endpoint was the objective response rate per Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) 1.1.
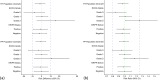
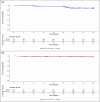
Results: Between 23 September, 2020 and 16 September, 2022, 690 patients were recruited (n = 345 each to BP02/RT). At the end of the induction phase (intent-to-treat population), a similar proportion of patients achieved an objective response rate with BP02 (n = 231 [67.0%], 95% confidence interval [CI] 62.0, 71.9) and RT (n = 238 [69.0%], 95% CI 64.1, 73.9). The 95% CI of risk difference (-2.03, 95% CI -9.15, 5.09) and 90% CI of risk ratio (0.97, 90% CI 0.89, 1.06) were within equivalence margins of ± 13% and (0.80, 1.25), respectively. Treatment-emergent adverse events leading to treatment withdrawal were reported in 2.9% and 3.2% patients with BP02 and RT, respectively.
Conclusions: BP02 showed an equivalent efficacy and similar safety profile to RT at the end of 24 weeks.
Clinical trial registration: CTRI Number: CTRI/2020/04/024456.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Arpitkumar Prajapati and Disha Dadke are employees of CuraTeQ Biologics Pvt Ltd. Rushab Kothari has received honoraria from Zydus Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Glenmark, Novartis, Emcure, Fresenius Kabi, Bard Peripheral Vascular, Pfizer, Alkem Laboratories, and Roche; has received institutional honoraria from Cipla, Merck, Celon Pharma, and Bristol Myers Squibb Foundation; served in a consulting/advisory role for MSD; and has received institutional research funding from Zydus Pharmaceuticals, Lambda Therapeutic Research, Axis Clinicals, and Reliance Life Sciences. M.V.T. Krishna Mohan, Rushabh Kothari, Srikrishna Mandal, R Srikanth, Rajnish Nagarkar, Shriram Khane, A Santa have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. 10.3322/caac.21660. - PubMed
-
- Exman P, Tolaney SM. HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer: a comprehensive review. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2021;19(1):40–50. - PubMed
-
- Kumar RV, Panwar D, Amirtham U, et al. Estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 status in breast cancer: a retrospective study of 5436 women from a regional cancer center in South India. South Asian J Cancer. 2018;7(1):7–10. 10.4103/sajc.sajc_211_17 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

