The positive impact of honeybee activity on fennel crop production and sustainability
- PMID: 38937513
- PMCID: PMC11211493
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-64283-2
The positive impact of honeybee activity on fennel crop production and sustainability
Abstract
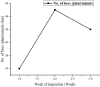
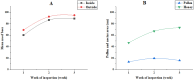
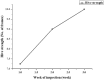
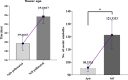
This study investigates the ecological interaction between honeybees (Apis mellifera) and fennel (Foeniculum vulgare) plants, examining the mutual benefits of this relationship. Field experiments conducted in Egypt from December 2022 to May 2023 recorded diverse insect pollinators attracted to fennel flowers, especially honeybees. Assessing honeybee colonies near fennel fields showed improvements in sealed brood (357.5-772.5 cells), unsealed brood (176.3-343.8 cells), pollen collection (53.25-257.5 units), honey accumulation (257.5-877.5 units), and colony strength (7.75-10) over three weeks. Fennel exposure explained 88-99% of variability in foraging metrics. Comparing open versus self-pollinated fennel revealed enhanced attributes with bee pollination, including higher flower age (25.67 vs 19.67 days), more seeds per umbel (121.3 vs 95.33), bigger seeds (6.533 vs 4.400 mm), heavier seeds (0.510 vs 0.237 g/100 seeds), and increased fruit weight per umbel (0.619 vs 0.226 g). Natural variation in seed color and shape also occurred. The outcomes demonstrate the integral role of honeybees in fennel agroecosystems through efficient pollination services that improve crop productivity and quality. Fennel provides abundant nutritional resources that bolster honeybee colony health. This research elucidates the symbiotic bee-fennel relationship, underscoring mutualistic benefits and the importance of ecological conservation for sustainable agriculture.
Keywords: Foeniculum vulgare; Agroecosystems; Apis mellifera; Crop production; Egypt; Food crops; Food production; Fruit weight; Funnel; Honeybees; Insect pollination; Reproductive success; Self-pollination.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Bokelmann JM. Fennel (Foeniculum vulgare) In: Bokelmann JM, editor. Medicinal Herbs in Primary Care. Elsevier; 2022. pp. 335–340.
-
- Soumanou MM, Adjou ES. Sweet Fennel (Ocimum gratissimum) Oils. In: Preedy VR, editor. Essential Oils in Food Preservation, Flavor and Safety. Academic Press; 2016. pp. 765–773.
-
- Singh YV, Srivastava DK, Singh P, Varma SK, Kanthle AK, Mishra D. Effect of integrated nutrient management on growth parameters of fennel (Foeniculam valgare Mill) in inceptisol. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2018;7(03):1067–1072. doi: 10.20546/ijcmas.2018.703.127. - DOI
-
- Mehra N, Tamta G, Nand V. A review on nutritional value, phytochemical and pharmacological attributes of Foeniculum vulgare Mill. J. Pharmacognosy Phytochem. 2021;10(2):1255–1263. doi: 10.22271/phyto.2021.v10.i2q.13983. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

