Dyslipidemia in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes in a Rural Community in Ganadougou, Mali: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 38938445
- PMCID: PMC11210374
- DOI: 10.4236/jdm.2024.142012
Dyslipidemia in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes in a Rural Community in Ganadougou, Mali: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
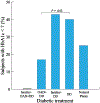
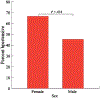
Dyslipidemia is a disorder where abnormally lipid concentrations circulate in the bloodstream. The disorder is common in type 2 diabetics (T2D) and is linked with T2D comorbidities, particularly cardiovascular disease. Dyslipidemia in T2D is typically characterized by elevated plasma triglyceride and low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels. There is a significant gap in the literature regarding dyslipidemia in rural parts of Africa, where lipid profiles may not be captured through routine surveillance. This study aimed to characterize the prevalence and demo-graphic profile of dyslipidemia in T2D in the rural community of Ganadougou, Mali. We performed a cross-sectional study of 104 subjects with T2D in Ganadougou between November 2021 and March 2022. Demographic and lipid profiles were collected through cross-sectional surveys and serological analyses. The overall prevalence of dyslipidemia in T2D patients was 87.5% (91/104), which did not differ by sex (P = .368). High low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) was the most common lipid abnormality (78.9%, [82/104]). Dyslipidemia was associated with age and hypertension status (P = .013 and.036, respectively). High total and high LDL-C parameters were significantly associated with hypertension (P = .029 and .006, respectively). In low-resource settings such as rural Mali, there is a critical need to improve infrastructure for routine dyslipidemia screening to guide its prevention and intervention approaches. The high rates of dyslipidemia observed in Gandadougou, consistent with concomitant increases in cardiovascular diseases in Africa suggest that lipid profile assessments should be incorporated into routine medical care for T2D patients in African rural settings.
Keywords: Cholesterol; Cross-Sectional Study; Dyslipidemia; Lipids; Mali; Type 2 Diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epidemiology of dyslipidemia and associated cardiovascular risk factors in northeast China: A cross-sectional study.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2020 Nov 27;30(12):2262-2270. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2020.07.032. Epub 2020 Aug 7. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 32988725
-
Lipid Screening in Childhood for Detection of Multifactorial Dyslipidemia: A Systematic Evidence Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force [Internet].Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2016 Aug. Report No.: 14-05204-EF-1. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2016 Aug. Report No.: 14-05204-EF-1. PMID: 27559550 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Serum lipid profiles including non-high density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in Turkish school-children.Anadolu Kardiyol Derg. 2007 Dec;7(4):415-20. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg. 2007. PMID: 18065339
-
Prevalence of Dyslipidemia and Availability of Lipid-Lowering Medications Among Primary Health Care Settings in China.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Sep 1;4(9):e2127573. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.27573. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 34586366 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Lipids During 20 Years in the Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study: Prevalence, Trends and Impact on Non-Communicable Diseases.Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Oct 16;16(4 Suppl):e84750. doi: 10.5812/ijem.84750. eCollection 2018 Oct. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2018. PMID: 30584435 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes in Africa. https://www.idf.org/our-network/regions-members/africa/diabetes-in-afric...
-
- Pappan N and Rehman A (2022) Dyslipidemia. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
